Prophecies And Protests ~ Eurocentric Versus Afrocentric Approaches: Management Thinking Beyond Dichotomies?
 Introduction
Introduction
In 2003 one of the authors of this article visited a historically disadvantaged university in South Africa where a colleague – a well known South African specialist on ubuntu – lectured in the Philosophy department at that time. The author gave a presentation on Genomics and Africa in one of the lecture rooms of the School of Molecular and Life Sciences of this university. On the wall outside the lecture hall there was a show case, containing a brochure of the school that stated:
Vision
The school of molecular and life sciences strives to be an internationally recognised afrocentric centre of excellence in biotechnology, arid zone studies, and related disciplines.
The author was struck by the use of the word ‘afrocentric’. Surely, molecular biology as such cannot be Afrocentric. Or can it? In Cell Biology International 2001, an article written by Barry Fabian was published. The title of his article was Cellular ubuntu: Umntu Ngumntu Ngabanye Abantu, and other problems for cell biologists in the new millennium. Fabian looked at the self-organisation of developing cells. He noted that the complexity of cells is not only related to the cell itself but also to the functional whole of cells leading to an ordered operating system. Fabian concluded: ‘To this end, cell and developmental biologists must continue to honour and explore the adage that “a cell only becomes a cell through other cells”’. So ‘molecular ubuntu’ in the metaphoric sense of the word is possible after all.
Afrocentricity is a concept that has gained popularity both in Africa and among African-Americans in North America. In this article we will first focus on the problems with regard to the definition of this concept. We will then argue that the popularity of the – loosely defined – concept is probably related to its metaphoric power, constructing an opposition to Eurocentric, and creating its own authenticity. We will try to demonstrate that this construction of opposition and authenticity, i.e. this construction of identity, can potentially mask other – possibly more relevant – dichotomies, notably the dichotomy between the rich and the poor.
Afrocentric: A definition problem
Trying to answer the question what afrocentric management is about, will undoubtedly induce problems of definition. Generally speaking, we find the term afrocentric difficult to handle because a clear and unambiguous definition of the concept seems to lack. Are we, for instance, talking about an African Afrocentrism or perhaps an African-American Afrocentrism, or are they both the same?
Afrocentricity is a concept that has a long history. It has been the subject of many discussions among African-American scholars in the United States for many years already. There is a wealth of literature related to this subject. One of its major advocates is the African-American scholar Molefi K. Asante. The Department of African American Studies of Temple University, where Asante has been working for many years, has been a leading place in spreading this concept. However, the concept of Afrocentricity has met with severe criticism from scholars, including Stephen Howe in his Afrocentrism: Mythical pasts and imagined homes (1999). Read more
Prophecies and Protests ~ Contextualising Ubuntu In The Glocal Management Discourse
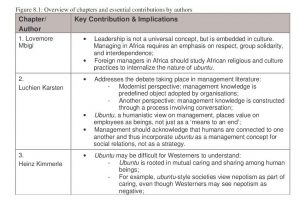
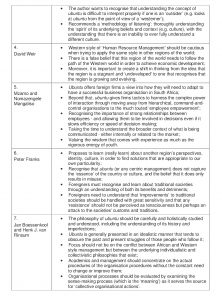
 The book ‘Prophecies and Protests: Ubuntu in Glocal Management’ provides a wealth of information on the unique Africa-centered management style based on ubuntu. While it is a monograph about anagement in Africa, it stops short of making the bold claim that Africa-centered management could be wider applicable, for example, in the Western world. However, the book alerts Western companies working in Africa to pay attention to the practices of ubuntu in African companies and its effects on the workforce. Since by definition ubuntu is a human condition, its emphasis on the social interactions of humans as a source of strength and meaning, provides a unique perspective on how leaders can create powerful organisations. A brief overview of the chapter contributions is captured in Table 1 for ease of reference.
The book ‘Prophecies and Protests: Ubuntu in Glocal Management’ provides a wealth of information on the unique Africa-centered management style based on ubuntu. While it is a monograph about anagement in Africa, it stops short of making the bold claim that Africa-centered management could be wider applicable, for example, in the Western world. However, the book alerts Western companies working in Africa to pay attention to the practices of ubuntu in African companies and its effects on the workforce. Since by definition ubuntu is a human condition, its emphasis on the social interactions of humans as a source of strength and meaning, provides a unique perspective on how leaders can create powerful organisations. A brief overview of the chapter contributions is captured in Table 1 for ease of reference.
In essence, ubuntu accentuates the notions of humaneness, sharing, and respecting all by creating great value for a group above pure individual desires and actions (Mangaliso 1992; 2001). It is a self-reinforcing set of beliefs that revolves around the core concept that the strength of any group resides in the relationship of its members. Behind this core concept are beliefs such as:
1. People are not just rational, self-interested beings, but are social beings whose interactions have implications for both the group and individuals within the group;
2. Unity of the whole is more fundamental than the distinction of the parts. Individuals do not act not in theoretical isolation – there is a reciprocal impact experienced within a network of social relationships;
3. Relationships are more important than any given decision or outcome;
4. Inclusiveness in decision-making is more important than speed or efficiency;
5. The broader context is always important, and ‘context’ could be on many levels: overall culture, human dynamics in a meeting, or non-verbal cues in a conversation;
6. The wisdom that comes with experience as valuable as the vigorous energy of youth;
7. Group performance is more important than individual ‘stars’; Strong individual performers are those that help the group the most. Read more
Hannah Arendt’s Theory of Totalitarianism – Part One
Hannah Arendt wrote The Origins of Totalitarianism in 1949, by which time the world had been confronted with evidence of the Nazi apparatus of terror and destruction. The revelations of the atrocities were met with a high degree of incredulous probing despite a considerable body of evidence and a vast caché of recorded images. The individual capacity for comprehension was overwhelmed, and the nature and extent of these programmes added to the surreal nature of the revelations. In the case of the dedicated death camps of the so-called Aktion Reinhard, comparatively sparse documentation and very low survival rates obscured their significance in the immediate post-war years. The remaining death camps, Majdanek and Auschwitz, were both captured virtually intact. They were thus widely reported, whereas public knowledge of Auschwitz was already widespread in Germany and the Allied countries during the war.[i] In the case of Auschwitz, the evidence was lodged in still largely intact and meticulous archives. Nonetheless it had the effect of throwing into relief the machinery of destruction rather than its anonymous victims, for the extermination system had not only eliminated human biological life but had also systematically expunged cumulative life histories and any trace of prior existence whatsoever, ending with the destruction of almost all traces of the dedicated extermination camps themselves, just prior to the Soviet invasion.
Although Arendt does not view genocide as a condition of totalitarian rule, she does argue that the ‘totalitarian methods of domination’ are uniquely suited to programmes of mass extermination (Arendt 1979: 440). Moreover, unlike previous regimes of terror, totalitarianism does not merely aim to eliminate physical life. Rather, ‘total terror’ is preceded by the abolition of civil and political rights, exclusion from public life, confiscation of property and, finally, the deportation and murder of entire extended families and their surrounding communities. In other words, total terror aims to eliminate the total life-world of the species, leaving few survivors either willing or able to relate their stories. In the case of the Nazi genocide, widespread complicity in Germany and the occupied territories meant that non-Jews were reluctant to share their knowledge or relate their experiences – an ingenious strategy that was seriously challenged only by Germany’s post-war generation coming to maturity during the 1960s. Conversely, many survivors were disinclined to speak out. Often, memories had become repressed for fear that they would not be believed, out of the ‘shame’ of survival, or because of the trauma suffered. Incredulity was thus both a prevalent and understandable human reaction to the attempted total destruction of entire peoples, and in the post-war era the success of this Nazi strategy reinforced a culture of denial that perpetuated the victimisation of the survivors. In The Drowned and the Saved Primo Levi records the prescient words of one of his persecutors in Auschwitz:
However this war may end, we have won the war against you; none of you will be left to bear witness, but even if someone were to survive, the world will not believe him. There will be perhaps suspicions, discussions, research by historians, but there will be no certainties, because we will destroy the evidence together with you. (Levi 1988: 11)
Here was unambiguous proof of the sheer ‘logicality’ of systematic genocide. The silence following the war was therefore quite literal, and the publication of Origins in 1951 could not and did not set out to bridge that chasm in the human imagination. It did, however, establish Arendt as the most authoritative and controversial theorist of the totalitarian. Read more
Hannah Arendt’s Theory of Totalitarianism – Part Two
Ideology and terror: The experiment in total domination
In chapter two of Hannah Arendt’s Response to the Crisis of her Time it was argued that Arendt’s typology of government rests on the twin criteria of organisational form and a corresponding ‘principle of action’. In the post-Origins essay On the Nature of Totalitarianism, Arendt argues that Western political thought has customarily distinguished between ‘lawful’ and ‘lawless’, or ‘constitutional’ and ‘tyrannical’ forms of government (Arendt 1954a: 340). Throughout Occidental history, lawless forms of government, such as tyranny, have been regarded as perverted by definition. Hence, if
… the essence of government is defined as lawfulness, and if it is understood that laws are the stabilizing forces in the public affairs of men (as indeed it always has been since Plato invoked Zeus, the god of the boundaries, in his Laws), then the problem of movement of the body politic and the actions of its citizens arises. (Arendt 1979: 466-7)
‘Lawfulness’ as a corollary of constitutional forms of government is a negative criterion inasmuch as it prescribes the limits to but cannot explain the motive force of human actions: ‘the greatness, but also the perplexity of laws in free societies is that they only tell what one should not, but never what one should do’ (ibid.: 467). Arendt, accordingly, lays great store by Montesquieu’s discovery of the ‘principle of action’ ruling the actions of both government and governed: ‘virtue’ in a republic, ‘honour’ in monarchy, and ‘fear’ in tyrannical forms of government (Arendt 1954a: 330; Arendt 1979: 467-8).
 In all non-totalitarian systems of government, therefore, the principle of action is a guide to individual actions, although fear in tyranny is ‘precisely despair over the impossibility of action’ since tyranny destroys the public realm of politics and is therefore anti-political by definition. Nevertheless, the state of ‘isolation’ and ‘impotence’ experienced by the individual in tyrannical forms of government springs from the destruction of the public realm of politics whereas the mobilisation of the ‘overwhelming, combined power of all others against his own’ (Arendt 1954a: 337) does not eliminate entirely a minimum of human contact in the non-political spheres of social intercourse and private life. Thus, if the fear-guided actions of the subject of tyrannical rule are bereft of the capacity to establish relations of power between individuals acting and speaking together in a public realm of politics, the ‘isolation’ of the political subject does not entail the destruction of his social and private relations (ibid.: 344). Therefore, in all non-totalitarian forms of government, the body politic is in constant motion within set boundaries of a stable political order, although tyranny destroys the public space of political action (Arendt 1979: 467).
In all non-totalitarian systems of government, therefore, the principle of action is a guide to individual actions, although fear in tyranny is ‘precisely despair over the impossibility of action’ since tyranny destroys the public realm of politics and is therefore anti-political by definition. Nevertheless, the state of ‘isolation’ and ‘impotence’ experienced by the individual in tyrannical forms of government springs from the destruction of the public realm of politics whereas the mobilisation of the ‘overwhelming, combined power of all others against his own’ (Arendt 1954a: 337) does not eliminate entirely a minimum of human contact in the non-political spheres of social intercourse and private life. Thus, if the fear-guided actions of the subject of tyrannical rule are bereft of the capacity to establish relations of power between individuals acting and speaking together in a public realm of politics, the ‘isolation’ of the political subject does not entail the destruction of his social and private relations (ibid.: 344). Therefore, in all non-totalitarian forms of government, the body politic is in constant motion within set boundaries of a stable political order, although tyranny destroys the public space of political action (Arendt 1979: 467).
Arendt argues that totalitarianism is distinguished from all historical forms of government, including tyranny, insofar as it has no use for any ‘principle of action taken from the realm of human action’, since the essence of its body politic is ‘motion implemented by terror’ (Arendt 1954a: 348; see 331-3). In other words, totalitarianism aims to eradicate entirely the human capacity to act as such (Arendt 1979: 467). For totalitarian rule targets the total life-world of its subjects, which in turn presupposes a world totally conquered by a single totalitarian movement.[i] Hence, only in
… a perfect totalitarian government, where all men have become ‘One Man’, where all action aims at the acceleration of the movement of nature or history, where every single act is the execution of a death sentence which Nature or History has already pronounced, that is, under conditions where terror can be completely relied upon to keep the movement in constant motion, no principle of action separate from its essence would be needed at all. (ibid.)
This important passage contains several key ideas that need to be carefully unpacked. Firstly, we encounter Arendt’s conception of society reduced to ‘One Man’ or a single, undifferentiated Mankind as a condition of a ‘perfect totalitarian government’. We may note here that totalitarianism thus conceived constitutes the very antithesis of the political in Arendt’s sense of men acting and speaking together in a public realm of politics. Secondly, Arendt contends that only in such a perfect totalitarian system would terror, which she views as the ‘essence’ of totalitarianism, suffice to sustain totalitarian rule. Hence, in all imperfect totalitarian dictatorships, terror in its dual function as the ‘essence of government and principle, not of action, but of motion’ (ibid.), is an insufficient condition of totalitarian rule. For, insofar as totalitarianism has not completely eliminated all forms of spontaneous human action, freedom, or the inherent human capacity to ‘make a new beginning’, exists as an ever-present potential within society (ibid.: 466).[ii] Totalitarian movements must therefore strive to eliminate this capacity for political action, and any form of spontaneous human relations. Hence:
What totalitarian rule needs to guide the behaviour of its subjects is a preparation to fit each of them equally well for the role of executioner and the role of victim. This two-sided preparation, the substitute for a principle of action, is the ideology. (ibid.: 468)
However – and this is a crucial point – Arendt stresses that it is
… in the nature of ideological politics … that the real content of the ideology (the working class or the Germanic peoples), which originally had brought about the ‘idea’ (the struggle of classes as the law of history or the struggle of races as the law of nature), is devoured by the logic with which the ‘idea’ is carried out. (Arendt 1979: 472) Read more
Hannah Arendt – Zur Person – Full Interview (with English Subtitles)
Hannah Arendt in the Rozenberg Quarterly
Anthony Court – Hannah Arendt’s Theory of Totalitarianism. Part One: http://rozenbergquarterly.com/?p=3099
Anthony Court – Hannah Arendt’s Theory of Totalitarianism. Part Two: http://rozenbergquarterly.com/?p=3115
Nima Emami – Hannah Arendt and The Green Movement: http://rozenbergquarterly.com/?p=563
Large Archive Of Hannah Arendt’s Papers Digitized By The Library Of Congress: Read Her Lectures, Drafts Of Articles, Notes & Correspondence
Many people read the German-Jewish political philosopher and journalist Hannah Arendt as something of an oracle, a secular prophet whose most famous works—her essay on the trial of Adolf Eichmann and her 1951 Origins of Totalitarianism—contain secrets about our own times of high nationalist fervor. And indeed they may, but we should also keep in mind that Arendt’s insights into the horrors of Nazism did not emerge until after the war.
Arendt did not identify as Jewish during the Nazi’s rise to power, but as a fully assimilated German; she had a romantic relationship with her professor Martin Heidegger, who became a doctrinaire Nazi, and she seemed to have little understanding of German antisemitism during the thirties and forties. Arendt, many have alleged, sometimes seemed too close to her subject.
The archives: http://www.openculture.com/2014/02/hannah-arendt-archives.html