Guan Zhixun & Fan Hong ~ Body and Politics: Elite Disability Sport in China
 There has been growing interest in research on disability sport internationally, yet little research has concentrated on the development of disability sport in China. This book focuses on elite disability sport in China in the context of history, politics, policies and practice from 1979 to 2012. It examines the relationship between athletes with disabilities and the three major disability games: the Paralympic Games, the Special Olympic Games and the Deaflympic Games. Three key questions are asked: What policies have ensured the success of elite disability sport? How do the elite sport system and management of elite disability sport work in China? In what way has elite disability sport empowered athletes with disabilities in China?
There has been growing interest in research on disability sport internationally, yet little research has concentrated on the development of disability sport in China. This book focuses on elite disability sport in China in the context of history, politics, policies and practice from 1979 to 2012. It examines the relationship between athletes with disabilities and the three major disability games: the Paralympic Games, the Special Olympic Games and the Deaflympic Games. Three key questions are asked: What policies have ensured the success of elite disability sport? How do the elite sport system and management of elite disability sport work in China? In what way has elite disability sport empowered athletes with disabilities in China?
The book includes a comprehensive literature review on the historical development of disability sport in China and beyond. Functionalism and empowerment are the major theoretical backgrounds for the research. The former analyses the function of elite sport policies, systems and other factors occurring during the process, whilst the latter examines the relationship of empowerment between elite disability sport and athletes in China. The three major disability competitions are used as case studies. A qualitative research methodology with specific methods of semi–structured interviews, data collection and documentary analysis is applied to the research. The thesis concludes that the development of elite disability sport in China has received strong support from the government. Elite disability sport is closely linked with China’s politics and international image. The success of athletes with disabilities on the international stage has raised the awareness of the issues facing people with disabilities. This has changed their image in Chinese society in general, and has empowered athletes with disabilities in particular. However, there is unbalanced development in elite disability sport. The book concludes by indicating some potential future directions for further research.
Nova Science Publishers, New York, 2018. Asian Studies. ISBN: 978-1-53613-510-7
Asian Studies (Series Editors: Fan Hong, Auke van der Berg and Peter Herrmann – Bangor University, UK, Rozenberg Quarterly, Netherlands and EURISPES – Istituto di Studi Politici, Economici e Sociali, Italy)
More information: https://novapublishers.com/shop/body-and-politics-elite-disability-sport-in-china/
Minako O’Hagan & Qi Zhang ~ Conflict And Communication: A Changing Asia In A Globalizing World – Language And Cultural Perspectives
 The chapters within this volume comprise selected papers from the 5th Annual Conference of the Asian Studies Irish Association (A.S.I.A.) held at Dublin City University in November 2013. Discussing the conference theme Conflict and Communication: A Changing Asia in a Globalising World, this volume presents multiple perspectives articulated by scholars across disciplines that include translation studies, language studies, literary studies and computer science.
The chapters within this volume comprise selected papers from the 5th Annual Conference of the Asian Studies Irish Association (A.S.I.A.) held at Dublin City University in November 2013. Discussing the conference theme Conflict and Communication: A Changing Asia in a Globalising World, this volume presents multiple perspectives articulated by scholars across disciplines that include translation studies, language studies, literary studies and computer science.
Within such disciplinary diversity emerged a unity which converged on language and culture as fundamental points of analysis. This volume covers research topics relating to China, Korea, Japan, Thailand, and Vietnam, as well as Asia as a whole in a globalising world. Insights shared by the ten authors each addressing Asia through a different disciplinary lens hope to provide future research impetus for students and established scholars alike within and beyond Asian Studies.
(Series Editors: Fan Hong, Auke van der Berg and Peter Herrmann – Bangor University, UK, Rozenberg Quarterly, Netherlands and EURISPES – Istituto di Studi Politici, Economici e Sociali, Italy)
Zhang Muchun & Fan Hong ~ The Sino-Indian Border War And The Foreign Policies Of China And India (1950-1965)
 There has been growing interest in the historical analysis of the Sino-Indian relations and the Sino-Indian border issue, yet little research has focused on the impact of two government’s foreign policies concerning the Sino-Indian border issue and border war. This book examines the Sino-Indian relations, particularly the Sino-Indian border issue and border war, Tibetan issues, and China and India’s foreign policies from the 1950s to 1960s. This book will discuss the origin and development of the Sino-Indian border issue and connections between national diplomatic policies and the border disputes in China and India.
There has been growing interest in the historical analysis of the Sino-Indian relations and the Sino-Indian border issue, yet little research has focused on the impact of two government’s foreign policies concerning the Sino-Indian border issue and border war. This book examines the Sino-Indian relations, particularly the Sino-Indian border issue and border war, Tibetan issues, and China and India’s foreign policies from the 1950s to 1960s. This book will discuss the origin and development of the Sino-Indian border issue and connections between national diplomatic policies and the border disputes in China and India.
More specifically, this book aims to illustrate the origins of the Sino-Indian border dispute, the role Tibet played in the Sino-Indian border issue, the impacts of their foreign policies on the Sino-Indian border issue from the 1950s to the 1960s, the measures both states took to ease boundary tensions and conflicts, the reasons for the outbreak of the 1962 Border War, and the changes to foreign policies the two governments made before and after the 1962 Border War. This book involves the collection and analysis of historical archival materials and official documents from both China and India.
The book is mainly aimed at researchers, undergraduates and postgraduate students in the subject areas of the history of international relations and Chinese studies. It could be used in a wide range of courses since it offers insights into the aspects of historical and international relations found within Chinese society. It will be of interest to academic libraries, research institutes, universities, and students either as a textbook or as reading material. Due to the appeal and relevance of the subject, this book would also be of interest to people who want to know more about the history of Sino-Indian border disputes as well as China and India’s foreign policies from 1950 to the 1960s through such a particular and appropriate topic.
Asian Studies (Series Editors: Fan Hong, Auke van der Berg and Peter Herrmann – Bangor University, UK, Rozenberg Quarterly, Netherlands and EURISPES – Istituto di Studi Politici, Economici e Sociali, Italy) – Nova Science Publishers, New York, 2018 – ISBN 978-1-53613-770-5
Got to: https://www.novapublishers.com/
The Rise And Fall Of The “Up To The Mountains And Down To The Countryside” Movement: A Historical Review
 Abstract
Abstract
The Up to the Mountains and Down to the Countryside (UMDC) Movement (上山下乡运动) was an important event in the history of the People’s Republic of China (PRC). It changed the fate of a whole generation of Chinese and had far-reaching effects on the history of the PRC. As a nationwide urban-to-rural migration (i.e. the reverse of the urbanization process), it is also unique in human history for its complex origin and the wide scope of its impact (16 million urban youths and nearly every Chinese family), as well as its long duration, tortuous process, and contradictory attributes. However, compared to the Cultural Revolution (1966–1976) and other political events of the 1960s, the UMDC Movement is rarely known to people who are unfamiliar with Chinese history. Even in the area of Chinese Studies, the UMDC Movement has been misunderstood as a constituent part or a ramification of the Cultural Revolution. This paper reviews the process of the development of the UMDC Movement and analyses the social structural factors in its rise and fall in Chinese history.
Introduction
From 1967 to 1979, more than 16 million[i] Chinese urban youths were sent to the countryside to engage in agricultural production. This was known as the Up to the Mountains and Down to the Countryside Movement (上山下乡运动). Those 16 million participants, who were named Zhiqing (educated youth 知青) after this movement, lived and worked in the countryside as ordinary agricultural labourers during their teenage years. In the early 1980s, when most Zhiqing eventually returned to the city, they were immediately faced with the residual issues of the UMDC Movement as well as the challenge of readjusting to urban society.
The UMDC Movement not only changed the fate of a whole generation of Chinese but also had far-reaching effects on the history of the People’s Republic of China. However, in overseas Chinese Studies, much less attention has been given to the UMDC Movement than to the Cultural Revolution (1966–1976). For many researchers, the UMDC Movement is a constituent part or a ramification of the Cultural Revolution.[ii] In terms of the relationship between the two historical events, the Zhiqing Office of the State Council announced an official conclusion in 1981:
“First of all, the ‘UMDC’ was a major experiment carried out by the Communist Party fromthe 1950s, based on fundamental realities of the country, which then had a large population, a weak economic foundation, and employment difficulties; it was not the result of the Cultural Revolution. Second, the ‘UMDC’ was aimed primarily at resolving employment problems; during the ten years of the Cultural Revolution, it evolved as a political movement under the ultra-left ideology and resulted in serious mistakes in practice.”[iii] (Gu 1997, pp. 283–285) Read more
Purifying Islamic Equities ~ The Interest Tax Shield
Abstract
This paper seeks to add to the debate regarding the appropriate methodology to purify tainted components from shari’ah compliant equities. Based on the Qur’anical prohibition against riba and an analysis of the purification methodology recommended by AAOIFI Shari’ah Standard 21, this paper highlights shortcomings in Standard 21 and references the corporate finance literature to argue for the need to also purify the interest tax shield from debt. Purification is a pivotal element of the Islamic investment process yet Standard 21 permits a loose interpretation which causes portfolios to be under-purified. Standard 21 also makes no mention of the interest tax shield from debt even though the benefits there from are at odds with the principles of social justice in Islam. That there is no mention of the interest tax shield from debt in the (limited) literature on the purification of Islamic equities is puzzling. This paper has implications for the Islamic funds industry as well as for compliant Muslim investors.
Introduction
The Islamic funds industry is estimated at 5.5 per cent (Ernst & Young, 2011) of the over $1.0 trillion (Wilson, 2009) global Islamic finance industry. Although small in comparison with the conventional funds industry, the potential growth from targeting the largely untapped Muslim market (estimated at 23 per cent of the world’s population) has garnered significant attention (Hassan and Girard, 2011). But the nascent Islamic funds industry is already at a crossroads. There are a number of issues which could derail its early promise – chief among these is confusion about how to purify Islamic portfolios to ensure shari’ah compliance.
Purification refers to the need to quantify and donate to charity all impure components deemed unacceptable under shari’ah principles and teachings (Elgari, 2000). Impure components include riba, which in modern Islamic finance has become synonymous with interest-related activity and is unequivocally prohibited in the Qur’an. Because nearly every company in the world receives/pays interest on its cash/debt balances, the practical effect of an absolute interpretation of the prohibition against riba is that the funds industry is, ipso facto, off limits for Muslim investors (Moore, 1997; McMillen, 2011). As a result, the shari’ah Supervisory Boards (hereafter SSBs) that determine the compliance of any investment have had to make a number of compromises to allow some permissible variation from absolute shari’ah principles. While some research has been done relating to the construction and application of Islamic stock screens, there is a paucity of literature about how haram elements resulting from permissible variation should be purified.[i],[ii] Although the Accounting and Auditing Organization for Islamic Financial Institutions (AAOIFI) recommends one method for purging impure amounts in Shari’ah Standard 21 Financial Papers (Shares and Bonds) (hereafter S21), the terminology used throughout is not consistent and, in certain sections, lacks specificity. Also, not all jurists adhere to AAOIFI standards such that several methods are used in practice. The result is that, even for those adhering to AAOIFI standards, differing interpretations are possible, meaning that confusion remains and haram components go unpurified. To some shari’ah scholars, the entire permissibility of an Islamic fund hinges on purification, so this lacuna needs to be addressed (Elgari, 2000).
This paper discusses the unequivocal prohibition against riba in the Qur’an and the hadith, and its impact on commercial activity in the Islamic world. It documents how the practice of permissible variation has evolved in the Islamic funds industry to allow a degree of deviation from absolute concepts and analyses some of the various current methodologies suggested for purging the consequent impurities from Islamic portfolios, with a focus on S21. Given what is at stake for the nascent Islamic funds industry, this chapter also suggests a comprehensive methodology for the purification of prohibited components which includes the need to also purify the benefits from the interest tax shield from debt −the benefits of which to the firm are well understood in the corporate finance literature.
Islam and Commercial Activity
Islam is a complete way of life, a lifestyle which constitutes a part of every Muslim’s cultural and spiritual identity (Abbasi, Holman,andMurray, 1989; DeLorenzo, 2002). Islam aims at striking a balance between individual freedoms (including commercial activities, Qu’ran 62:10) and ensuring that these freedoms are conducive to the growth and benefit of society at large (Ebrahim, 2003). Indeed, the Qur’an and the Sunnah (Islamic custom and practice) place tremendous stress on justice. All leading jurists therefore, without exception, have held that justice is a central indispensable ingredient of the maqasid al-shari’ah, or the goals of Islam (Chapra, 2000). In economics, justice can be interpreted to mean that resources are used in a manner that ensures, inter alia, the equitable distribution of income and wealth and economic stability (Chapra, 2000). Since the emergence of post-independence Muslim states in the global economy in the 1960s, there has been much debate about how commercial activity, and for this chapter the Islamic funds industry specifically, can be organized to conform to Islamic justice and shari’ah. Chapra (2000) contends that these goals cannot be realized without a humanitarian strategy which injects a moral dimension into economics — the prohibition against riba is part of this moral dimension. Read more
The Case Of “Fukushima” ~ Notation Choice As A Highlighting Device In Ad Hoc Concept Construction
 Abstract
Abstract
The irregular use of katakana has been analysed mainly in descriptive terms and is often considered to be a device for creating homonyms or communicating emotions (See Ogakiuchi, 2010). This chapter examines the irregular use of katakana notation from the perspective of relevance theory. Unlike previous studies, which have focused on the images and emotions the katakana notation system is said to communicate, this chapter focuses on concepts communicated by the use of words when they are written in katakana rather than other usual notations. I show that the irregular use of katakana is just one of many devices used for highlighting ad hoc concepts that can be found universally and should be analysed in a wider context than describing the functions of this notation,which is unique to Japanese. I argue that a cognitively grounded relevance theoretic account, in particular the notions of ad hoc concepts and metarepresentation, enables us to provide an explanation for observations made in previous studies.
The paper concludes that emotions attributed to the use of katakana and the homonyms which katakana notation appears to create can be explained in terms of repeated metarepresentation of ad hoc concepts and attributed thoughts communicated by the concepts.
Introduction –The Japanese Writing System
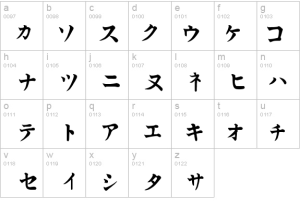
The Japanese writing system uses three different types of notation. The first is kanji, which is logographic. Each kanji character has a “meaning” and is used for conceptual words. There are also two alphabet systems, hiragana and katakana. Hiragana is phonographic and used for particles, connectives, and other “function words”, as well as being used by children (and adults) when they do not know which kanji to use. Katakana is also phonographic and is mainly used for loan words, onomatopoeia, and the names of animals, species, flowers, etc. It is convention that all three notation systems are used as required. Example (1) demonstrates this:
(1) ジョンの 庭にネコが 入ってきた.
John no niwa ni neko ga haitte kita
John GEN garden LOC cat SUB entered
“A cat came into John’s garden.”
In (1), two conceptual words,“garden”and “enter”, are written in kanji: 庭 and 入, respectively. Hiragana is used for particles,“no” (の) and “ni” (に), part of verb conjugation (ってきた), and the subject marker“ga” (が). Although they are conceptual words, katakana is used for “John” (ジョン) and “cat” (ネコ) as John is non-Japanese and “cat” is the name of an animal.
The choice of notation system is based on this convention and one’s ability – if one does not know or remember how to write a certain kanji, one might choose to write the word in hiragana or katakana. This is particularly the case for children and in hand-written texts. This paper does not aim to analyse these cases, where choice of notation is based on personal abilities. Nor does it deal with cases where katakana notation is used as it is expected to be. Instead, this study will focus on cases where the use of katakana cannot be explained in terms of personal abilities or preferences. In particular, I shall focus on cases in which katakana is used where it is not expected or not because of personal preference/abilities. A particular focus will be placed on correlations between choice of notation and construction of ad hoc concepts, where the use of katakana seems to trigger concept adjustment. See “Fukushima”in (2)[i]:
(2) チェルノブイリからフクシマへ「同じ道たどらないで」
Chernobyl kara Fukushima e “onaji michi tadoranaide”
Chernobyl FROM Fukushima LOC “same road follow-NEG-IMPERATIVE”
From Chernobyl to Fukushima: “Please do not go the way we did”
(Sekine 2011)
“Fukushima” is the name of a town and, normally, it is written as 福島 in kanji. However, in (2), it is written as フクシマ in katakana, and it seems to communicate more than just a name. What does it communicate? How is it different from “Fukushima” written in kanji? In following sections, I will first look at how katakana notation has been dealt with in previous studies and then present an alternative account from the perspective of relevance theory. Read more