Wildfires Aren’t Just A Threat To People—They’re Killing Off Earth’s Biodiversity

Reynard Loki – Photo: Independent Media Institute
Cataclysmic wildfires have increased in intensity and frequency due to climate change.
In early August 2023, a succession of wildfires ignited within the state of Hawaii, primarily affecting the island of Maui. It is considered “one of the worst natural disasters in Hawaii’s history, and the nation’s deadliest wildfires since 1918.” Driven by powerful winds, these fires sparked urgent evacuations, inflicted extensive devastation, and tragically claimed the lives of at least 115 individuals—though the final confirmed death toll may never be known due to the severity of the fires and the lack of DNA evidence to identify the victims. In the town of Lāhainā, as many as 850 people were reported missing by Hawaii officials as of August 21. The rapid spread of these wildfires was linked to the arid, gusty weather conditions generated by a robust high-pressure system located north of Hawaii, combined with the influence of Hurricane Dora from the southern region. This nightmare scenario in Hawaii is not unique.
In 2020, the catastrophic wildfires that raged across California, Oregon, and Washington state consumed around 5 million acres of dry forest. “I drove 600 miles up and down the state, and I never escaped the smoke,” Senator Jeff Merkley (D-Or) said on the ABC News television show “This Week” on September 13, 2020. “We have thousands of people who have lost their homes. I could have never envisioned this.”
The firefighters on America’s West Coast were battling the deadly blazes as the 75th session of the United Nations General Assembly convened in September 2020 at the UN headquarters in New York. One of the high-level meetings as part of the session was the Summit on Biodiversity. Strikingly, the hot-button issue of wildfires was not mentioned in the event program, even though wildfires continue to pose a direct threat to biodiversity across the planet. According to the Living Planet Report 2020 by the World Wildlife Fund (WWF), populations of monitored mammals, fish, birds, reptiles, and amphibians have collectively dwindled by nearly 70 percent worldwide from 1970 to 2016. The underlying cause: humanity.
Wildfires’ Impact on Biodiversity
The Hawaiian rainforests of Kauai once teemed with ‘akikiki, small songbirds cloaked in gray plumage. But when humans came to the island, they inadvertently introduced mosquitoes carrying avian malaria. “With no immunity to the disease, ‘akikiki and other native songbirds began to die off. The species’ population crashed in the early 2000s, and today, the situation is so dire that scientists estimate just five ‘akikiki exist in the wild in Kauai,” stated an August 2023 article in the Smithsonian Magazine.
The species’ survival is in the hands of scientists on a nearby island, at the Maui Bird Conservation Center, which houses approximately 40 ‘akikiki and actively encourages them to breed in captivity, according to the article. This facility also provides shelter to around 40 ‘alalā, the Hawaiian crow, which has vanished from its natural habitat. Thankfully, the center’s avian residents were rescued from the August wildfires. Still, the episode highlights the increasing risk wildfires pose to the survival of wildlife, particularly the danger they cause to species already on the brink of extinction.
Cataclysmic wildfires—the intensity and frequency of which have increased due to human-caused climate change—are not just an American phenomenon. In the summer of 2023, catastrophic wildfires swept through Maui, Greece, Italy, Spain, Portugal, Algeria, Tunisia, and Canada. And wildfires impact far more than human life, trees, and the built environment; Countless wild animals have perished in the flames. “[A]s many as 1.25 billion animals—including iconic Australian species such as koalas, kangaroos, wallabies, and gliders—have been killed or displaced by the fires,” Earth | Food | Life (EFL) reporter Robin Scher wrote on Truthout in April 2020 about Australia’s “Black Summer,” the colloquial name of the 2019-2020 Australian bushfire season, which was unusually intense. “In some instances, certain species may have even gone extinct,” Scher reported.
Writing about the Amazon wildfires for Truthout, EFL reporter Daniel Ross noted in June 2020 that the “illegal logging, encroachment from agribusinesses, and profit-driven government policies,” that underpin Brazil’s wildfires, impacted wildlife, threatened Indigenous communities, and created an air pollution-related health crisis in the nation’s urban areas. The fires even spread into virgin forests in the country.
Wildfires Linked to Cattle Farming
In addition, the fires—many of which are illegally started to create pasture for cows that supply Brazil’s multibillion-dollar beef industry—have created a dangerous situation for the global climate. “[R]esearch suggests that some deforested regions of the rainforest are exhaling more carbon dioxide than they’re taking in,” Ross reported.
And make no mistake, a rapidly and unnaturally changing climate is a direct threat to the planet’s biodiversity, and to the variety of life on Earth that provides the foundation for a host of life-supporting ecological services—such as clean air, clean water, healthy soil, and crops, plant pollination, pest control, wastewater treatment, and outdoor recreation.
A Vicious Cycle
There is a vicious cycle at work: While wildfires are destroying biodiversity, biodiversity loss may contribute to increased susceptibility to wildfires. According to a 2016 study published in the journal Animal Conservation, the extinction of medium-sized, ground-dwelling mammals in Australia could be a factor that primes the bush to burn more easily.
“Australia has seen the extinction of 29 of 315 terrestrial mammal species in the last 200 years and several of these species were ecosystem engineers whose fossorial actions may increase the rate of leaf litter breakdown,” wrote Matt Hayward, the lead author of the report, and his co-authors, in the report’s abstract. “Thus, their extinction may have altered the rate of litter accumulation and therefore fire ignition potential and rate of spread.”
Hayward argued that restoring biodiversity could help reduce the likelihood of wildfires starting and spreading rapidly.
Advocacy Groups Call for Action
Some organizations are fighting against the indiscriminate deforestation resulting from cattle farming activities that have fueled the wildfires in the Amazon forest. Amnesty International reported that “63 percent of the [Brazilian Amazon] deforested from 1988 to 2014 has become pasture for cattle—a land area five times the size of Portugal.” The group has called for ending illegal cattle farming in the Amazon. “Illegal cattle ranching is the main driver of Amazon deforestation. It poses a very real threat, not only to the human rights of Indigenous and traditional peoples who live there but also to the entire planet’s ecosystem,” said Richard Pearshouse in 2019, when he was the head of crisis and environment at Amnesty International.
Care2 launched a public petition in 2020 urging the Brazilian government to stop allowing these human-created fires destroying the Amazon rainforest. As of July 2023, the petition has garnered more than 122,000 signatures.
In 2020, Brazilian meat giant JBS pledged it would introduce, by 2025, a new system to monitor both its direct and indirect cattle suppliers. However, Amnesty criticized the announcement, saying the “timeline [was] too far removed.” The group pointed out that “JBS has been aware of the risks that cattle illegally grazed in protected areas may enter its supply chain since at least 2009, and previously pledged to monitor its indirect suppliers by 2011.”
Sustainable Environment Named a ‘Human Right’
In October 2021, the United Nations Human Rights Council (UNHRC) recognized for the first time “that having a clean, healthy, and sustainable environment is a human right.” The proposed text, put forth by Costa Rica, the Maldives, Morocco, Slovenia, and Switzerland, was approved with 43 votes in favor and four abstentions. The abstaining countries were Russia, India, China, and Japan.
Michelle Bachelet, who was at the time the UN High Commissioner for Human Rights, had long supported the move. After the vote, she said “that she was ‘gratified’ that the decision ‘clearly recognizes environmental degradation and climate change as interconnected human rights crises,’” adding that “Bold action is now required to ensure this resolution on the right to a healthy environment serves as a springboard to push for transformative economic, social and environmental policies that will protect people and nature.”
BirdLife International, a global partnership of non-governmental organizations working to conserve birds and their habitats, while seeking a resolution by the UN General Assembly reaffirming the rights recognized by the UNHRC, said that “to emerge from [the climate and biodiversity]… crises, to ensure our future and that of the planet, we need to entirely transform humanity’s relationship with nature. This human right helps make that happen.”
Wildfires Predicted to Increase
“The choking smoke cast a dark pall over the skies and created a vision of climate-change disaster that made worst-case scenarios for the future a terrifying reality for the present,” reported the New York Times about the wildfires that blazed across the Western United States in 2020. That terrifying reality could go on for generations if we don’t get a handle on the climate crisis.
In September 2022, climate journalist and native Oregonian Emma Pattee wrote in the New York Times that “[c]limate scientists estimate that the frequency of large wildfires could increase by over 30 percent in the next 30 years and over 50 percent in the next 80 years, thanks in large part to drought and extreme heat caused by climate change.” That is a frightening prospect not just for humans but for the countless nonhuman animals with whom we share this planet.
Byline:
Reynard Loki
Author Bio:
Reynard Loki is a co-founder of the Observatory, where he is the environment and animal rights editor. He is also a writing fellow at the Independent Media Institute, where he serves as the editor and chief correspondent for Earth | Food | Life. He previously served as the environment, food, and animal rights editor at AlterNet and as a reporter for Justmeans/3BL Media covering sustainability and corporate social responsibility. He was named one of FilterBuy’s Top 50 Health and Environmental Journalists to Follow in 2016. His work has been published by Yes! Magazine, Salon, Truthout, BillMoyers.com, Asia Times, Pressenza, and EcoWatch, among others.
Source:
Independent Media Institute
Credit Line:
This article was produced by Earth | Food | Life, a project of the Independent Media Institute.
Sustainability Is Not As New An Idea As You Might Think—It’s More Than 300 Years Old

Erika Schelby – Academia.edu
Modern sustainability evolved from forest management of the 18th century, and its ancient roots go back even further. Could it help with today’s climate crisis and lumber shortage?
The proverb “necessity is the mother of invention” has roots that go back to Aesop’s fable “The Crow and the Pitcher” and to Plato’s “Republic.” It is realistic to assume that Hans Carl von Carlowitz, mining manager for the Saxon court in Freiberg, Germany, during the late 17th and early 18th centuries, was also driven by necessity and a severe shortage of wood to invent the concept of sustainability (“Nachhaltigkeit”).
Or to be more precise, he coined the word to describe the quintessential principles of a human activity that goes back to the dawn of history: the sustainable use of natural resources. Although it may not have been called sustainability until Carlowitz, societies had practiced it for a long time as a vital part of cultural or religious practices. Ancient Egypt pursued sustainable systems for more than 3,000 years. The Maya, according to anthropologist Lisa Lucero, practiced a “cosmology of conservation.” The literature of ancient India is brimful with references to the preservation of the environment.
On the other hand, there are ancient civilizations that may have collapsed because they despoiled the natural world that gave them life. The earliest example may be found in the ancient Mesopotamian “Epic of Gilgamesh,” the first version of which dates back to 2000 B.C. Clay tablets tell the tale of vast cedar forests cut down by the eponymous hero in defiance of the gods, who punish him by cursing the land with fire and drought, turning the region into a desert. Nothing grew anymore, forcing the Sumerians to flee to Babylon and Assyria.
Now, 300 years after Carlowitz gave sustainability its modern name when Europe was short on wood, we have again experienced a timber shortage—this one triggered by the COVID-19 pandemic and caused by climate change.
The modern concept of sustainable living on a planet with limited resources evolved from the work done by Carlowitz regarding the need for the sustainable management of forests.
In 1713, just a year before his death, Carlowitz published the 432-page folio book, Sylvicultura Oeconomica oder Anweisung zur wilden Baum-Zucht(“Silvicultural Oeconomica or the Instructions for Wild Tree Cultivation”).
Sylvicultura Oeconomica documented the beginning of scientific forestry. It also invented sustainability, which had to be accepted to assure the continuity of human societies and of nature. Without scientific forestry, people across Europe and around the world would have faced far more severe economic and social disasters than the ones witnessed in the last few centuries. “In the beginning was the Earth,” said Christof Mauch, a modern-day German sustainability specialist and historian, in a 2013 lecture. “The Earth does not need humans to survive, but humans need the Earth.”
In fact, Carlowitz envisioned the three pillars of sustainability: environmental, economic, and social justice. He rejected short-term thinking. He offered solutions, scientific details, guidelines and practical proposals on how to save, select, nurse, plant, re-grow, maintain and protect forests and their biodiversity. He presented an inventory of conditions across Europe and discussed threats caused by extreme weather conditions, diseases, pests and humans. He pled for careful, frugal consumption and recommended the art of saving timber. His ideas for using energy-efficient stoves in housing or furnaces in smelters, tips on improving the insulation in buildings, and finding substitutes like peat for heating homes are not unlike today’s sustainability efforts. The main part of the book deals with the urgent work that needs to be done to overcome the Holznot, or wood emergency. In his 2010 book, German journalist Ulrich Grober calls Sylvicultura Oeconomica “the birth certificate of our modern concept of sustainability.”
These concepts developed by Carlowitz have been adopted across the globe in the course of the last 300 years. Unfortunately, today the rapid deforestation of large areas continues unabated in various regions, mostly in the Global South. The developed Global North had already done much of its massive deforestation during the era of industrialization. It should be noted that today, the greed of wealthy individuals, corporations and governments from the rich countries often exacerbate the climate crisis in tropical regions, while Indigenous peoples and those who are not in positions of power due to lack of access to capital or being located in the Global South (particularly island nations) often have proven, long-term sustainable forest management and environmental practices and are most affected by the unsustainable practices of developed nations.
But the rich world has been reeling from the climate impacts of unsustainable development for decades, with increasing temperatures and a rise in the frequency and intensity of extreme weather events. In many ways, we are losing a race against time. During the summer of 2021 in the United States, firefighters wrapped aluminum foil around the trunk of a giant old sequoia, hoping to save the world’s largest tree from “a raging wildfire” in California. Sequoias, which can live for up to 3,400 years, have coexisted with occasional forest fires for millennia. They don’t burn easily and have survived wildfires over the years, even benefitting from fires that clear away the underbrush, creating new space and providing the required sunlight for seedlings. But this no longer works. The new wildfires of the climate change era last too long and burn too hot even for these huge trees, who were once regarded as invulnerable. According to the New York Times, “in last year’s Castle fire, between 7,000 and 11,000 large sequoias died across the Sierra Nevada or about 10 to 14 percent of them.”
All these natural calamities have come in a cluster, bundled together in the last few years: the pandemic, ever more and ever bigger forest fires in the West and leaping north into Canada, excessive heat, lasting drought and the destruction of millions of trees by a tiny creepy-crawly bark-eating beetle. Businesses closed their doors, sawmills halted production, truckers stopped trucking and logistical bottlenecks multiplied. Builders ceased construction and people were stuck in lockdowns at home.
Then, contrary to expectations, a DIY frenzy broke out. Confined to their houses or apartments because of pandemic-related restrictions, Americans started to improve their private spaces. Perhaps they felt it was the only reality they could count on. It was something they valued as a zone of safety and personal freedom in the midst of turmoil: a room of one’s own.
Wood became a high-demand commodity. Trading at $381 for 1,000 board feet back in 2019, in May of 2021 lumber hit a record high of $1,711.20. Costs for lumber have come down again, but house prices have not. According to the National Association of Home Builders (NAHB), “the average price of a newly constructed single-family home has increased by about $ 36,000 since April of 2020.”
It’s a vicious cycle: trees are stressed by heat and drought, which makes them less resilient. A cold climate used to keep the mountain pine beetles under control but warming temperatures have upset the balance and increased their numbers. With more mouths to feed, the beetles advanced into new areas, attacked weakened trees, and have already devastated 27 million hectares of forest across North America “an area more than three quarters the size of Germany.”
There are also more and more people who are directly confronted by climate change. The Washington Post reports that “[n]early 1 in 3 Americans live in a county hit by a weather disaster in the past three months… On top of that, 64 percent live in places that experienced a multiday heat wave.”
So how long can people function and be productive under the present and increasingly worse circumstances? How can governments govern? When will the governed discover that the powerful Wizard of Oz isn’t so mighty after all?
Americans are still embedded in a never-ending stream of the same-old growth and consumption messages that contradict what society as a whole must do to become sustainable. But finally, there is a shift in public awareness. According to the Yale Program on Climate Communication, “three out of four Americans now believe that global warming is happening today.” It is hard to tell if this change of mind will last; public opinion is fickle, and there is the fact of a short attention span.
Perhaps it is helpful to acknowledge that the world was in trouble before, and that, driven by necessity 300 years ago, it found solutions. The challenges being faced by people across the globe are far bigger today, but the tools available to them are better too. The world has added much science, and people should have a better understanding of how nature and societies work.
Three scientists were awarded and share the Nobel Prize for physics 2021: Syukuro Manabe of Princeton, Klaus Hasselmann of the Max Planck Institute in Hamburg, Germany, and Giorgio Parisi of the Sapienza University of Rome, Italy. All three of them did long-term groundbreaking work related to complex physical systems and modeling the Earth’s climate.
Hans Carl von Carlowitz had no access to such advanced science. All he had was his observation, the science of his time, and a bold mind. But he would most certainly agree with the physicist Giorgio Parisi, who commented on the timing of the awarding of the Nobel Prize in physics to climate change researchers: “It is clear that for the future generations, we have to act now in a very fast way and not with a strong delay.” We’ve had sustainability concepts for more than 300 years—it’s certainly past time to utilize them.
Byline:
Erika Schelby
Erika Schelby is a contributor to the Observatory and author of Looking for Humboldt and Searching for German Footprints in New Mexico and Beyond (Lava Gate Press, 2017) and Liberating the Future from the Past? Liberating the Past from the Future? (Lava Gate Press, 2013), which was shortlisted for the International Essay Prize Contest by the Berlin-based cultural magazine Lettre International. Schelby lives in New Mexico.
Source:
Independent Media Institute
Credit Line:
This article was produced by Earth | Food | Life, a project of the Independent Media Institute.
Profit Trumps People And Planet In Brazil’s Eucalyptus Industry
 Brazil is set to unleash several varieties of genetically engineered eucalyptus, which will worsen a bad situation.
Brazil is set to unleash several varieties of genetically engineered eucalyptus, which will worsen a bad situation.
Valued for its termite-resistant wood for building purposes, pulp to create products like writing and toilet paper, and its oil, which has numerous health and household benefits, the eucalyptus tree generates big business worldwide. Native to Australia and Tasmania, the prehistoric tree has been planted in such volumes that eucalyptus plantations cover some 25 million hectares around the globe—larger than the entire land area of the United Kingdom. By 2028, according to forecasts, the global eucalyptus oil market is projected to exceed $213 million, while the worldwide market for eucalyptus pulp will expand to nearly $17 billion.
But the eucalyptus industry has a dark side. Eucalyptus plantations growing in regions spanning South America, southern Africa, southern Europe, and Australia have significant detrimental impacts on local communities and biodiversity. Communities located near eucalyptus plantations are likely to face water shortages—as these plantations utilize huge amounts of water—and pollution from agrochemicals, including exposure to glyphosate, which has been linked to various health problems, including increased cancer risk.
In addition, the presence of eucalyptus trees’ leaves and roots hinders the growth of other plants beneath them because they contain a biocidal oil that inhibits the survival and decomposition of most soil bacteria that come into contact with them.
Brazil is the world’s largest eucalyptus producer. With an estimated 7.6 million hectares of eucalyptus plantations, Brazil maintains 30 percent of the world’s total eucalyptus trees. In eastern Brazil, particularly in the states of Bahia and Espírito Santo, these plantations have replaced the diverse and endemic Atlantic Forest ecosystem, with some municipalities seeing nearly three-quarters of their land area being covered by eucalyptus plantations. Large corporations such as Suzano, Fibria, and Veracel dominate this industry, exporting eucalyptus as pulp for manufacturing products like toilet paper.
New Forest Threat: Genetically Engineered Eucalyptus
Genetically engineered (GE) varieties of eucalyptus trees are poised to exacerbate a new wave of ecological and social destruction. Brazil has approved seven varieties of genetically engineered trees. Current plantations rob regions of water, destroy wildlife habitat, and transform large swaths of land within the Cerrado—an expansive, biodiverse tropical biome situated in eastern Brazil—into unnatural, destructive monoculture farms: rows upon rows of non-native eucalyptus trees without vegetation in their understory. Many traditional communities and Indigenous people have opposed the spread of these plantations in the country.
Varieties of GE eucalyptus are pesticide-resistant and are likely to increase the use of toxic chemicals such as Roundup, the glyphosate-based weedkiller developed by Monsanto in the 1970s, which is the world’s most used herbicide—and was acquired by Bayer in 2018. Other engineered traits, such as increased growth rates, could make the trees more profitable for the pulp and paper industry but significantly more harmful to the environment.
International Opposition to GE Eucalyptus
The Campaign to STOP GE Trees is an international alliance of organizations working to halt the introduction of genetically engineered trees into the natural environment to prevent ecological destruction and harm to local communities. It is an initiative of our U.S.-based organization, Global Justice Ecology Project (GJEP), with support from the Uruguay-based World Rainforest Movement, which advances the cause of social justice in the forests.
An international delegation of the campaign, which was organized by GJEP, traveled to Brazil in July 2023 to meet with Indigenous and quilombola communities (descendants of escaped Afro-Brazilian enslaved people), members of the Landless Workers’ Movement (Movimento dos Trabalhadores Rurais Sem Terra, or MST, in Portuguese), government ministries, and academics. The delegation’s goal was to learn about the history of resistance against the pulp and paper industry in the country and discuss how herbicide-resistant genetically engineered varieties of eucalyptus trees could increase the use of toxic herbicides and amplify ecological degradation, health impacts, and social injustice.
FASE (Federação de Órgãos para Assistência Social e Educacional), a group that has been supporting communities opposing eucalyptus plantations for a decade, organized the logistics of the delegation, which included representatives from Argentina, Canada, Chile, Ireland, Japan, New Zealand, and the United States. Local representatives joined the delegation as it visited several Brazilian ministries to register official demands and testimonies from quilombola and MST community members from northern Espírito Santo and southern Bahia about the devastating impacts of eucalyptus plantations as well as new threats posed by GE eucalyptus trees.
“The demands that we recorded were from several MST communities that we met with that are doing important agroecological work and have a whole agroecological school training people in the region about how to grow organically,” said Anne Petermann, international coordinator of the Campaign to STOP GE Trees. She noted that “there were also statements from members of traditional quilombola communities in that region who are suffering, very directly, the impacts of eucalyptus plantations.”
The delegation also officially presented petitions from Rainforest Rescue, an environmental nonprofit based in Hamburg, Germany, signed by more than 100,000 people opposing the release of GE eucalyptus in Brazil to the ministries and Brazilian National Technical Commission on Biosafety.
During the delegation’s official meeting, Moisés Savian, secretary of Brazil’s Ministry of Agrarian Development, identified corporate interests driving the push for GE eucalyptus.
“It makes no sense in my vision to have a transgenic [eucalyptus] associated with glyphosate,” stated Savian. His comments highlighted the increasingly ubiquitous and dangerous as well as probable cancer-causing herbicide Roundup. “It is much more linked to market interests of the corporations that want to sell herbicide,” the secretary noted.
The Kafkaesque Incentive of Carbon Credits
Another motivation behind the push for GE eucalyptus is the Kafkaesque incentive of receiving carbon credits for planting trees. Corporations like Suzano—which has been called the “world’s largest pulp exporter”—can be rewarded for planting enormous industrial tree monocultures—since they are technically planting trees, they are eligible for carbon credits—even though they first clear-cut and remove the carbon-dense native forests, which release vast amounts of carbon from the forest and the soil.
The pulp industry in Brazil has accelerated the growth rate of their eucalyptus trees. This is increasing the already enormous demands on water resources. So problematic is the expansion of eucalyptus monocultures on the hydrology and biodiversity of regions that they are often called “green deserts.”
“They look green from a distance but are extremely fast-growing trees planted in perfect rows and columns optimal for mechanical harvesting. The huge plantations do not harbor wildlife, and the only biodiversity you find in them is ants and termites,” explained Petermann, who led the delegation that traveled to Brazil.
One of the most insidious trends in false solutions to climate change is the idea that living or biological carbon can offset fossil fuel carbon. An expanding landscape of monoculture industrial tree plantations in Brazil—which rob the forests of biodiversity, displace communities and wildlife, and deplete regions of water resources—epitomizes the eco-swindle of carbon credits.
João, a member of a quilombola community, told the delegation that when eucalyptus started being planted in Espírito Santo and Bahia, “they removed the native plant cover and all the nutrients from the soil. People [here] used to do agroforestry, would use cover crops, [and would] let the land rest—but now, with eucalyptus, there is no rest for the soil.” The total eucalyptus plantation area in Bahia is estimated to be about 658,000 hectares, positioning it as the country’s third-largest contributor to industrially cultivated eucalyptus.
Dr. Ricarda Steinbrecher, a biologist from the University of London who attended a forum hosted by the delegation, warned of unintended consequences of genetically engineered trees, stating that “the risks of GE trees is extremely high in terms of the impact on biodiversity, the people living around it, and the global ecosystem and climate.”
Not only are current eucalyptus plantations destructive, but the premise that they are superior to natural forests for capturing carbon is also unsound. In 2020, experts published a letter with the Institute of Physics stating that “forests are superior to, and irreplaceable by, plantations as agents of terrestrial C [carbon] sequestration.” They are harvested with incredibly short growing cycles for pulp and paper production, which releases the carbon back into the atmosphere. But the scheme is profitable for Suzano and other pulp companies since they profit from the production of pulp and paper as well as carbon credits for planting trees.
Private Military Companies Continue To Expand In Africa

Photo: eng.wikipedia.org
The recent coup in Niger threatens to unleash more private military and security companies on a continent where they have become steadily more powerful in recent decades.
In the wake of the July 26 coup in Niger, the world’s spotlight has once again turned to the expansion of private military and security companies (PMSCs) across Africa. Following the removal of the relatively pro-Western government, Niger’s new military rulers asked Russian PMSC Wagner to help defend against a possible military intervention by the Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS), with U.S. Secretary of State Antony Blinken warning of the PMSC seeking to exploit the instability.
In a continent marked by decades of post-colonial turmoil, PMSCs have steadily gained influence, evolving from their historical role as mercenaries into powerful, corporate-driven forces. As the Sahel region continues to grapple with instability and conflict, the strengthening of PMSCs, both domestic and foreign, will continue to reshape Africa’s security in profound and unpredictable ways.
Africa’s experience with PMSCs dates back to the decolonization period after World War II. Though mercenaries had been steadily sidelined in conflicts for centuries, rag-tag groups of privateers emerged as shadowy accomplices to colonial powers, aiding in suppressing rebellions and fomenting unrest while providing a degree of ambiguity. Britain’s “Mad Mike” Hoare and France’s Bob Denard came to exemplify this era through their active involvement in military operations that undermined the sovereignty of African states.
The end of the Cold War ushered in a new chapter for PMSCs. With millions of demobilized soldiers seeking employment and civil conflicts on the rise in the early 1990s, these entities evolved into more corporate forms. The South African PMSC Executive Outcomes (EO), founded in 1989 by Eeben Barlow, gained notoriety by accepting contracts to protect energy infrastructure in Angola and to fight Sierra Leone’s civil war.
Pressure from South Africa’s post-apartheid government led to the disbandment of EO in 1998. But other PMSCs had emerged, including Sandline International, also financed by EO backer Anthony Buckingham and Canadian businessman Rakesh Saxena, that helped gain control over mineral rights in Sierra Leone. And after Washington began to lean heavily on PMSCs during the wars in Afghanistan and Iraq, the taboo of using them was broken.
Existing in a legal gray zone, PMSCs have leveraged their strategic capabilities worldwide—no more so than in Africa. Fragile government institutions, powerful criminal and militant groups, international power struggles, and competition over Africa’s natural resources have nurtured an environment supportive of a growing network of PMSCs. Across the continent, they are used to secure energy facilities, government buildings, and private infrastructure, protect local actors and foreign personnel, and provide police and military training, intelligence, and active fire support to governments and corporate clients.
Through entities like the colossal PMSC Wagner, Russia has found an unconventional and effective way to assert influence in Africa’s security landscape. In the Sahel region, Russian PMSCs have filled a void left by departing French military forces and capitalizing on local anti-French sentiment in recent years.
Amid shifting allegiances, Wagner underscores how Russia’s indirect power projection allows the Kremlin to wield substantial influence without deploying conventional military forces. Wagner’s activities are believed to span across Mali, Sudan, Zimbabwe, Angola, Madagascar, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Mozambique, Burkina Faso, Chad, the Central African Republic (CAR), and the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC). Other Russian PMSCs, such as RSB Group, Moran Security Group, and Patriot, also operate across Africa.
At the center of Russia’s PMSC network in Africa stands Yevgeny Prigozhin, Wagner’s financier. The Russian tycoon celebrated the success of the coup in Niger and declared Wagner capable of handling the situation, though the Russian government declined to support it. Despite Prigozhin’s longstanding quarrels with the Russian military, which culminated in his insurrectionist march toward Moscow in June, Prigozhin was recently seen meeting with African dignitaries on the side of the Russia-Africa summit in St Petersburg.
As the Nigerien government grapples with its situation, Wagner could again act as a Kremlin surrogate, safeguarding Russia’s interests by filling the security vacuum left by the ousted French military. Already, there are fears that Niger may halt uranium exports, vital to both French and EU supplies, and forcing the West’s attention to the country. Russian media has criticized Prigozhin since his rebellion and officials have downplayed state connections to Wagner’s activities in Africa. But Prigozhin’s ongoing role in Africa suggests the Kremlin is relying on smoke and mirrors to obscure its true motivations.
Beyond Russia, numerous Western PMSCs have embedded themselves within Africa’s security. Unlike Russia’s PMSCs, most do not operate on the frontlines of conflict and primarily operate in security and training roles, though do coordinate with official military deployments. French PMSC Secopex made headlines in 2011 when its founder was killed in Libya during the country’s revolution, and it remains unclear as to what the PMSC’s role was.
Secopex had also been involved in the CAR and Somalia, while Corpguard (also created by the co-founder of Secopex, David Hornus) has been involved in training the Cote D’Ivoire’s military.
Other French PMSCs, such as Agemira, are active in the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC). Though French-owned, Agemira is registered in Bulgaria to take advantage of the country’s lack of regulation and transparency. The UK’s Aegis Defence Services is believed to have worked in 18 African countries, while G4S, Erinys, and Olive Group are also active in Africa.
U.S. PMSCs have been active across the continent since the 2000s, with MPRI, CACI International, and Academi (previously the notorious Blackwater) among the most notable. Others, such as DynCorp, have provided training and logistical support to Liberia, Sudan, and Somalia, while Triple Canopy has been active in Niger. AdvanFort Co in turn offers anti-piracy maritime protection in East and West Africa. Germany’s Xeless and Asgaard are also active in Africa, with the latter having operations in Sudan, Libya, Mauritania, and Egypt.
PMSCs have increasingly begun to operate in the same conflict zones. Somalia, which lacked a functional state for more than two decades, provided fertile ground for PMSC expansion. PMSCs from the U.S., UK, China, UAE, and even Norway have helped Somalia train its official government forces and provide maritime protection from piracy and terrorism and ensure stability. But in Libya, PMSCs from or backed by Russia, France, the UK, the U.S., Turkey, the United Arab Emirates (UAE), and more have all been sent to the country since 2011 to exploit the chaos and advance their interests.
Active in Libya, Turkey’s SADAT group has also signed deals to train African troops while pitching itself as a Muslim alternative PMSC for Islamic-majority countries. The UAE-based Black Shield Security Company was accused in 2020 of promising Sudanese citizens security contractor jobs but instead sent them to conflict zones in Libya. Other UAE PMSCs have been active in East Africa, including in Somalia, while China has developed a multitude of PMSCs to secure its Belt and Road projects in Africa. Israeli PMSCs have their own African operations.
In 2014, the Nigerian government began hiring PMSCs to help defeat the Boko Haram insurgency. One of them, Specialized Task, Training, Equipment, and Protection (STTEP), was also set by EO’s Barlow and saw significant success that helped grant it additional contracts. Other modern South African PMSCs include Osprey, Blackhawk, and Dyck Advisory Group, the latter of which was hired by Mozambique to combat Al-Shabaab militants but was accused of killing civilians indiscriminately by the UN in 2020.
The use of PMSCs in Africa is likely to expand. They often offer African governments a quick, relatively inexpensive, and tailored way to manage crises instead of relying on ineffective state forces. PMSCs also enable international companies to protect themselves without relying on the fanfare of official military deployments by working with another corporate entity.
Nonetheless, this raises questions about sovereignty, a recurring issue in a continent where it has consistently been violated since African countries won their independence. The monopoly on the use of violent force by their police and military institutions has been steadily eroded by criminals, militants, foreign countries, and increasingly, PMSCs.
The dangers of commodifying security are evident. Foreign companies and powerful local actors can afford security, while the core issues of instability in countries or regions are not addressed. Furthermore, instability is often used by outside forces to their advantage. Many Africans also end up working for PMSCs outside the continent because they are cheaper than recruits from other parts of the world.
Furthermore, PMSCs, and the governments and companies that employ them, remain largely uncommitted to stronger regulation. The Montreux Document aimed to enforce greater rules for PMSCs, but has been criticized for its limited scope and lack of binding nature. Other countries, including the five members of the UN Security Council, have refused to ratify the UN International Convention Against the Recruitment, Use, Financing, and Training of Mercenaries.
Criticism of PMSCs in Africa is growing. In February 2023, the African Union (AU) commissioner for political affairs, peace, and security, Bankole Adeoye, called for the “complete exclusion of mercenaries from the African continent.” But U.S. PMSC Bancroft Global had already been hired by the AU to assess the risk of Somali forces trained by Blackwater founder Erik Prince to continue operating in the country.
These entities epitomize globalization. Aegis Defence Services was acquired by Canadian company GardaWorld in 2015, while DynCorp was bought by Amentum in 2020. Academi and Triple Canopy merged in 2014 to form Constellis Group, while Triple Canopy has outsourced work to Peru-based PMSC Defion International. Erik Prince, through the Hong Kong-based Frontier Services Group, has helped China train its own PMSCs for use in Africa and elsewhere. G4S was meanwhile bought by Allied Universal in 2021 and is now North America’s third-largest private employer. Allied Universal itself is owned by institutional investor Caisse de dépôt et placement du Québec and private equity firm Warburg Pincus.
Many PMSCs provide legitimate and needed security for civilians and government officials. But considering the wide-ranging motivations, means, and methods of so many PMSCs on the continent—and increasingly in the same spaces—it is critical for Africa’s governments, leaders, and populations to consider how comfortable they are in allowing this rapidly developing global PMSC network to continue expanding in their own backyards.
Byline:
Author Bio:
This article was produced by Globetrotter.
John P. Ruehl is an Australian-American journalist living in Washington, D.C. He is a contributing editor to Strategic Policy and a contributor to several other foreign affairs publications. His book, Budget Superpower: How Russia Challenges the West With an Economy Smaller Than Texas’, was published in December 2022.
Source:
Globetrotter
How The US Supreme Court Became An Arm Of The Republican Party
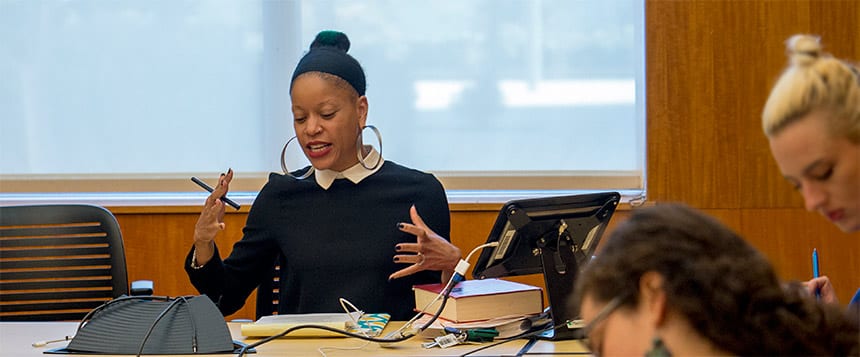
Professor Khiara M. Bridges worked with students from the Reproductive Rights and Justice seminar she taught last semester on an amicus brief for an abortion rights case the U.S. Supreme Court will hear in March. Photo: law.berkeley.edu
The court is making decisions based on the GOP platform, not the Constitution, says legal scholar Khiara M. Bridges
The U.S. Supreme Court, whose current ideological leanings are extremely reactionary, has spearheaded a broad national regression on human rights. Indeed, the United States is a global outlier on multiple fronts (the only wealthy nation without a universal health care system and number one in firearms per capita, to name just a few), and some of the latest Supreme Court rulings (on abortion, guns and affirmative action) are turning the country into “a global pariah.”
How do we make sense of these utterly dangerous developments? First of all, why is the Supreme Court acting like the executive committee of the Republican Party? Are there even clean legal arguments upon which its rulings are based? In this exclusive interview for Truthout, renowned law professor and anthropologist Khiara M. Bridges, who specializes in the intersection of race, class, reproductive justice and law, shares her insights into the issues raised above and offers some legal remedies that she believes will help achieve racial justice and equality in the 21st century.
Bridges is a professor of law at UC Berkeley School of Law. Her scholarship has appeared in scores of prestigious publications, including the Harvard Law Review, the Stanford Law Review, the California Law Review, the NYU Law Review and the Virginia Law Review. She is the author of Reproducing Race: An Ethnography of Pregnancy as a Site of Racialization (2011), The Poverty of Privacy Rights (2017) and Critical Race Theory: A Primer (2019). On July 12, 2022, Bridges testified before the U.S. Senate Judiciary Committee about the fallout from the U.S. Supreme Court’s recent decision in Dobbs v. Jackson Women’s Health Organization, which overturned Roe v. Wade.
C. J. Polychroniou: Race, class and gender have functioned as organizing principles in the development of U.S. society and culture from the very beginning and continue to shape social identities to this day. Your own work, as a professor of law and an anthropologist, focuses on the relationship between race, class and gender in the context of reproductive rights and law. Can you briefly discuss this relationship and explain what intersectionality has to do with efforts to create a more equitable and just world for ourselves and future generations?
Khiara M. Bridges: I will try to answer your question by explaining why I was drawn to the study of the intersection of race, class and gender in the context of reproductive rights and law.
When I was in law school, I was struck by the way pregnancy and motherhood were described in Supreme Court cases. On the whole, the court talked about pregnancy and motherhood in celebratory terms. They were conceptualized as good for the pregnant woman, her family, her community and the nation as a whole. Language idealizing pregnancy and motherhood could be found even in cases in which the court protected the right to terminate a pregnancy. For example, in Planned Parenthood v. Casey, in which the court affirmed its holding in Roe v. Wade that the Constitution protected the right to terminate a pre-viability pregnancy, the court writes:
‘As with abortion, reasonable people will have differences of opinion about these matters. One view is based on such reverence for the wonder of creation that any pregnancy ought to be welcomed and carried to full term no matter how difficult it will be to provide for the child and ensure its well-being. Another is that the inability to provide for the nurture and care of the infant is a cruelty to the child and an anguish to the parent.’
Here, even in its defense of the constitutional right to abortion, the court speaks about pregnancy and motherhood in radiant terms. In this framing, the abortion right deserves recognition and protection because when pregnancy occurs during a disadvantageous time in a person’s life — when they do not have the means to provide for the child’s emotional and material needs — it is “cruel” to the infant and causes the parent “anguish.” In my reading, the court still conceptualizes pregnancy as a blessing. The court recognizes a constitutional right to abortion simply because this blessing may occur at a bad time.
The fairly laudatory presentation of pregnancy and motherhood in the court’s jurisprudence sits in diametrical opposition to the way that some people’s pregnancies are spoken about in political discourse. When I was in law school, the nation had just spent the two immediately preceding decades talking about “welfare queens” — implicitly Black women who were imagined to have babies solely to increase the size of their welfare checks. “Welfare queens” were decidedly bad for the nation; they drained public finances while producing children that were the country’s future criminals and “welfare queens” themselves. I was in law school during a period of time in which politicians were arguing that welfare beneficiaries should be required to take long-acting reversible contraception, or to undergo sterilization, in order to receive financial assistance from the state. Essentially, politicians were talking about poor people’s reproduction as if it were a social problem that needed to be solved. This was, again, the complete inverse of the way that the court spoke about pregnancy and motherhood.
I was fascinated by the inversion. And race and class explain the opposition. They explain why some people’s procreation is celebrated, and other people’s procreation is denigrated. And that’s really the lesson of intersectionality. Intersectionality offers a framework for understanding the complexity of social life. It recognizes that power is exerted along many different axes in the U.S. — race, class, sex, gender identity, sexuality, ability, immigration status, religion etc. And intersectionality simply submits that privilege or subjugation will look different at the various intersections of those axes of power. So, for example, sexism when it intersects with race privilege will look different than the way it looks when it intersects with race un-privilege. The form that sexism, patriarchy and misogyny have taken for affluent white women is the command to reproduce at all costs. The form that sexism has taken for Black women, especially when they are poor, is the demand that they avoid reproduction at all costs.
And so, intersectionality cautions that as we engage in efforts to create a more equitable and just world, we have to be careful not to allow one group’s experiences with an axis of power to stand in for everyone’s experience with that axis of power. If we do, our efforts will be liberatory only for some.
Critical race theory was developed in the 1980s but has become a hot-button political issue for today’s conservatives in the U.S. What is it about critical race theory that has become such an obsession for Republicans, and why is it coming up now?
You are absolutely correct to note that critical race theory was developed in the 1980s. It was created by law professors who were trying to figure out how it came to be that dramatic racial inequality endured even though the civil rights movement of the 1950s and 1960s had forced the nation to bestow formal racial equality onto people of color. The Civil Rights Act of 1964 and the Voting Rights Act of 1965 both had been passed. These were monumental pieces of legislation. Nevertheless, when these incipient critical race theorists looked around at the social landscape in the 1980s, they saw that people of color were still at the bottom of most measures of social well-being. Black people, particularly, were incarcerated at higher rates than white people; they were poorer than white people; they were sicker than white people; they died earlier than white people. So, the law professors who created critical race theory wanted to think about how this dramatic racial inequality could coexist with formal racial equality. That is what critical race theory sets out to do. It is an advanced legal theory that attempts to think through the relationship between law and continuing racial injustice in a post-civil rights era.
Of course, this is not what the Republican Party is talking about when they invoke “critical race theory.” Conservative pundits and politicians say that critical race theory is being taught in K-12 schools. They say that it is “Marxist.” They say that it proposes that all white people are racist and all Black people are oppressed. Essentially, their description of critical race theory bears absolutely no relationship to actual critical race theory — the advanced legal theory that law professors began developing in the 1980s. Essentially, the Republican Party has co-opted the term, and they are using the struggle to rid so-called critical race theory from public life to accomplish the goal of silencing any talk that suggests that racial inequality remains a problem and that race still matters in the U.S. today.
I think that it is important to keep in mind precisely when the Republican Party began talking about critical race theory. The GOP’s fixation began in fall 2020 — right after the country had a long, hot summer of racial protests in the wake of George Floyd’s murder. If you recall, optimists that summer were saying that the country was having a “racial reckoning.” Then, in the fall, the Republican Party began claiming that critical race theory was being taught everywhere — to federal employees, kindergartners and everyone in between. The timing is no accident. It seems pretty obvious that the Republican Party created a bogeyman out of critical race theory to stop whatever racial reckoning that was happening at the time and to undo any gains — legislative, political, discursive — that racial justice advocates had managed to achieve that summer.
Finally, it is important to understand the intentionality behind the creation of “critical race theory” as a bogeyman. Most scholars thinking through the Republican Party’s co-optation of the term “critical race theory” credit Christopher Rufo, a conservative activist, with putting so-called critical race theory on the Republican Party’s radar. In March 2021, Rufo tweeted:
‘We have successfully frozen their brand — “critical race theory” — into the public conversation and are steadily driving up negative perceptions. We will eventually turn it toxic, as we put all of the various cultural insanities under that brand category.
The goal is to have the public read something crazy in the newspaper and immediately think “critical race theory.” We have decodified the term and will recodify it to annex the entire range of cultural constructions that are unpopular with Americans.’
Very rarely do the villains explicitly and publicly reveal their nefarious plans. In this case, the villain did just that.
The Supreme Court’s Republican-appointed majority has issued a series of ultra-reactionary rulings on a number of critical issues such as voting rights, affirmative action, gerrymandering, abortion, gun control and campaign finance. Are these rulings based on clear legal arguments, or are they in fact driven by political preferences and ideological biases? For example, there seems to be very little consistency in the Supreme Court decisions on guns and abortion.
I think that it is hard for anyone to say with a straight face that the court’s recent decisions are based on clear, consistent legal principles. I believe that anyone paying attention sees that the court has been issuing decisions that are consistent only in the sense that they consistently align with the Republican Party’s political platform.
What’s Happening In Niger Is Far From A Typical Coup

Vijay Prashad
On July 26, 2023, Niger’s presidential guard moved against the sitting president—Mohamed Bazoum—and conducted a coup d’état. A brief contest among the various armed forces in the country ended with all the branches agreeing to the removal of Bazoum and the creation of a military junta led by Presidential Guard Commander General Abdourahamane “Omar” Tchiani. This is the fourth country in the Sahel region of Africa to have experienced a coup—the other three being Burkina Faso, Guinea, and Mali. The new government announced that it would stop allowing France to leech Niger’s uranium (one in three lightbulbs in France is powered by the uranium from the field in Arlit, northern Niger). Tchiani’s government revoked all military cooperation with France, which means that the 1,500 French troops will need to start packing their bags (as they did in both Burkina Faso and Mali). Meanwhile, there has been no public statement about Airbase 201, the U.S. facility in Agadez, a thousand kilometers from the country’s capital of Niamey. This is the largest drone base in the world and key to U.S. operations across the Sahel. U.S. troops have been told to remain on the base for now and drone flights have been suspended. The coup is certainly against the French presence in Niger, but this anti-French sentiment has not enveloped the U.S. military footprint in the country.
Interventions
Hours after the coup was stabilized, the main Western states—especially France and the United States—condemned the coup and asked for the reinstatement of Bazoum, who was immediately detained by the new government. But neither France nor the United States appeared to want to lead the response to the coup. Earlier this year, the French and U.S. governments worried about an insurgency in northern Mozambique that impacted the assets of the Total-Exxon natural gas field off the coastline of Cabo Delgado. Rather than send in French and U.S. troops, which would have polarized the population and increased anti-Western sentiment, the French and the United States made a deal for Rwanda to send its troops into Mozambique. Rwandan troops entered the northern province of Mozambique and shut down the insurgency. Both Western powers seem to favor a “Rwanda” type solution to the coup in Niger, but rather than have Rwanda enter Niger the hope was for ECOWAS—the Economic Community of West African States—to send in its force to restore Bazoum.
A day after the coup, ECOWAS condemned the coup. ECOWAS encompasses fifteen West African states, which in the past few years has suspended Burkina Faso and Mali from their ranks because of the coups in that country; Niger was also suspended from ECOWAS a few days after the coup. Formed in 1975 as an economic bloc, the grouping decided—despite no mandate in its original mission—to send in peacekeeping forces in 1990 into the heart of the Liberian Civil War. Since then, ECOWAS has sent its peacekeeping troops to several countries in the region, including Sierra Leone and Gambia. Not long after the coup in Niger, ECOWAS placed an embargo on the country that included suspending its right to basic commercial transactions with its neighbors, freezing Niger’s central bank assets that are held in regional banks, and stopping foreign aid (which comprises forty percent of Niger’s budget). The most striking statement was that ECOWAS would take “all measures necessary to restore constitutional order.” An August 6 deadline given by ECOWAS expired because the bloc could not agree to send troops across the border. ECOWAS asked for a “standby force” to be assembled and ready to invade Niger. Then, ECOWAS said it would meet on August 12 in Accra, Ghana, to go over its options. That meeting was canceled for “technical reasons.” Mass demonstrations in key ECOWAS countries—such as Nigeria and Senegal—against an ECOWAS military invasion of Niger have confounded their own politicians to support an intervention. It would be naïve to suggest that no intervention is possible. Events are moving very fast, and there is no reason to suspect that ECOWAS will not intervene before August ends.
Coups in the Sahel
When ECOWAS suggested the possibility of an intervention into Niger, the military governments in Burkina Faso and Mali said that this would be a “declaration of war” not only against Niger but also against their countries. On August 2, one of the key leaders of the Niger coup, General Salifou Mody traveled to Bamako (Mali) and Ouagadougou (Burkina Faso) to discuss the situation in the region and to coordinate their response to the possibility of an ECOWAS—or Western—military intervention into Niger. Ten days later, General Moussa Salaou Barmou went to Conakry (Guinea) to seek that country’s support for Niger from the leader of the military government in that country, Mamadi Doumbouya. Suggestions have already been floated for Niger—one of the most important countries in the Sahel—to form part of the conversation of a federation that will include Burkina Faso, Guinea, and Mali. This would be a federation of countries that have had coups to overthrow what have been seen to be pro-Western governments that have not met the expectations of increasingly impoverished populations.
The story of the coup in Niger becomes partly the story of what the communist journalist Ruth First called “the contagion of the coup” in her remarkable book, The Barrel of the Gun: Political Power in Africa and the Coup d’états (1970). Over the course of the past thirty years, politics in the Sahel countries has seriously desiccated. Parties with a history in the national liberation movements, even the socialist movements (such as Bazoum’s party) have collapsed into being representatives of their elites, who are conduits of a Western agenda. The French-U.S.-NATO war in Libya in 2011 allowed jihadis groups to pour out of Libya and flock into southern Algeria and into the Sahel (almost half of Mali is held by al-Qaeda-linked formations). The entry of these forces gave the local elites and the West the justification to further tighten limited trade union freedoms and to excise the left from the ranks of the established political parties. It is not as if the leaders of the mainline political parties are right-wing or center-right, but that whatever their orientation, they have no real independence from the will of Paris and Washington. They became—to use a word on the ground—“stooges” of the West.
Absent any reliable political instruments, the discarded rural and petty-bourgeois sections of the country turn to their children in the armed forces for leadership. People like Burkina Faso’s Captain Ibrahim Traoré (born 1988), who was raised in the rural province of Mouhoun, and Colonel Assimi Goïta (born 1988), who comes from the cattle market town and military redoubt of Kati, represent these broad class fractions perfectly. Their communities have been utterly left out of the hard austerity programs of the International Monetary Fund, of the theft of their resources by Western multinationals, and of the payments for Western military garrisons in the country. Discarded populations with no real political platform to speak for them, these communities have rallied behind their young men in the military. These are “Colonel’s Coups”—coups of ordinary people who have no other options—not “General’s Coups”—coups of the elites to stem the political advancement of the people. That is why the coup in Niger is being defended in mass rallies from Niamey to the small, remote towns that border Libya. When I traveled to these regions before the pandemic, it was clear that the anti-French sentiment found no channel of expression other than hope for a military coup that would bring in leaders such as Thomas Sankara of Burkina Faso, who had been assassinated in 1987. Captain Traoré, in fact, sports a red beret like Sankara, speaks with Sankara’s left-wing frankness, and even mimics Sankara’s diction. It would be a mistake to see these men as from the left since they are moved by anger at the failure of the elites and of Western policy. They do not come to power with a well-worked out agenda built from left political traditions.
The Niger military leaders have formed a twenty-one-person cabinet headed by Ali Mahaman Lamine Zeine, a civilian who had been a finance minister in a previous government and worked at the African Development Bank in Chad. Military leaders are prominent in the cabinet. Whether the appointment of this civilian-led cabinet will divide the ranks of ECOWAS is to be seen. Certainly, Western imperialist forces—notably the United States with troops on the ground in Niger—would not like to see this torque of coups remain in place. Europe—through French leadership—had shifted the borders of their continent from north of the Mediterranean Sea to south of the Sahara Desert, suborning the Sahel states into a project known as G-5 Sahel. Now with anti-French governments in three of these states (Burkina Faso, Mali, and Niger) and with the possibility of trouble in the two remaining states (Chad and Mauritania), Europe will have to retreat to its coastline. Sanctions to deplete the mass support of the new governments will increase, and the possibility of military intervention will hang over the region like a famished vulture.
Byline:
Vijay Prashad
Author Bio:
This article was produced by Globetrotter
Vijay Prashad is an Indian historian, editor, and journalist. He is a writing fellow and chief correspondent at Globetrotter. He is an editor of LeftWord Books and the director of Tricontinental: Institute for Social Research. He has written more than 20 books, including The Darker Nations and The Poorer Nations. His latest books are Struggle Makes Us Human: Learning from Movements for Socialism and (with Noam Chomsky) The Withdrawal: Iraq, Libya, Afghanistan, and the Fragility of U.S. Power.
Source:
Globetrotter


