May Day In Havana: International Solidarity To Resist The U.S. Blockade
 This year’s May Day celebration in Cuba was interrupted by severe storms that knocked out electricity in much of the country. Authorities had no choice but to postpone the traditional mass marches. But for over 150 young grassroots organizers from the United States who had traveled to the country to mark the holiday, this turn of events was just more reason to deepen their efforts to end the U.S.-imposed blockade of the country.
This year’s May Day celebration in Cuba was interrupted by severe storms that knocked out electricity in much of the country. Authorities had no choice but to postpone the traditional mass marches. But for over 150 young grassroots organizers from the United States who had traveled to the country to mark the holiday, this turn of events was just more reason to deepen their efforts to end the U.S.-imposed blockade of the country.
Miya Tada, a brigade participant from New York, explained how this showed that “the biggest obstacle the Cuban people are facing is the repression and economic warfare of our own government, and that just inspires me to further the struggle against the blockade back in the United States.”
This wide range of activists from nearly 30 states and dozens of organizations was brought together by the International Peoples’ Assembly, a network of left movements and parties around the globe. Members of the solidarity brigade had spent the preceding week taking part in educational panels, discussions with Cuban activists, and youth exchanges as they sought to deepen their understanding of the Cuban Revolution.
May Day Amid a Tightening Blockade
The country is currently grappling with a range of severe difficulties that boil down to a single tremendous challenge—surviving amid a blockade that seems to tighten every day. The U.S.-imposed blockade has been in effect for over six decades, but a series of developments in the past several years has taken its cruelty to new heights.
The COVID-19 pandemic caused havoc in every country on the planet, but the coercive measures on Cuba magnified the crisis dramatically there. The country was able to avoid the kind of catastrophic loss of life experienced in the United States thanks to its world-renowned health system that produced five different vaccines, but the economic consequences were grave. Tourism is a principal source of foreign currency—essential to import vital goods since Cuba is locked out of the dollar-dominated world market—but this industry effectively disappeared overnight. Many other sectors of the economy were severely impacted as well.
“The other pandemic we faced,” Dr. Damodar Peña Pentón of the Latin American School of Medicine explained to brigade members earlier in the trip, “was the administration of Donald Trump. He imposed 243 new measures and used COVID-19 as an ally.”
Over the course of the Trump administration, the mild thaw in U.S.-Cuba relations that took place at the end of the Obama years was completely reversed. Aiming to suffocate the revolution, Trump imposed 243 new restrictions on Cuba designed to totally isolate it from the world economy.
Towards the end of his term, the State Department officially labeled Cuba a “state sponsor of terrorism”—because it had hosted successful peace talks between the Colombian government and the rebel movement FARC! Colombia’s president at the time was celebrated for his efforts with a Nobel Peace Prize, but Cuba’s reward was to be slandered as terrorists in an effort to further deter potential trading partners. This is a prime example of what Johana Tablada, Deputy Director for U.S. Affairs at the Cuban Ministry of Foreign Affairs, told brigade members the prior week: “The U.S. government has been permanently telling lies to justify its policy.”
Last August, a massive inferno broke out at the country’s main fuel storage facility in the province of Matanzas. A lightning strike sparked a fire that exploded one of the facility’s massive tanks and then spread to three more. Fourteen firefighters tragically died as they heroically battled the blaze.
Such a disaster would badly affect any country, but for Cuba, the blockade had already made it extraordinarily hard to meet its energy needs. Severe fuel shortages ensued, which persist to this day. This disrupts daily life in innumerable ways and makes it extremely difficult to respond to situations like the storm on the eve of May Day.
Just a few weeks after the fire, on September 27th, Hurricane Ian made landfall in the western province of Pinar del Río. The powerful storm destroyed over 50,000 homes and damaged 60 percent of the housing in the province. Construction materials desperately needed for reconstruction efforts could not be imported due to the economic siege of the island.
Ian also had a profound effect on agriculture. Pinar del Río is known for its tobacco production, and Cuba’s cigars are an important way to acquire foreign currency through exports. Food crops being grown in the region were almost totally destroyed.
The cumulative effect of all this was to create an economic crisis that—contrary to the presentation in the major corporate media outlets—is the consequence of the limitless cruelty of the U.S. government, not a failure of socialism.
The United States seeks to cover up this criminal behavior by preventing its own citizens from traveling to Cuba to see the reality firsthand. Despite traveling as part of a licensed, completely legal trip, members of the youth brigade were harassed and held in secondary questioning upon their return home at the Miami and Newark airports. Several young activists had their phones wrongfully searched and seized in a blatant violation of their civil liberties.
Moving Forward Despite Great Obstacles
The slogan of this year’s May Day in Cuba was “Hands and Hearts for the Homeland!” It reflects the urgent need for every Cuban to contribute all their abilities to overcome any challenge.
Any easing of U.S. pressure on the country will be an immense relief as they pursue this task. The blockade of the country has been almost unanimously condemned at the United Nations on an annual basis for three decades. But even short of the full lifting of the blockade, steps like the revocation of the 243 Trump-imposed measures or the outrageous designation by the State Department that Cuba is a “state sponsor of terrorism” would improve the situation greatly.
“Being here in Cuba has opened my eyes to the dire need in the United States to raise awareness about what’s going on with this blockade and to end it,” explained brigade member Sarah Brummet of Pensacola, Florida. “I’m very inspired to see the solidarity and the struggle of the Cuban people, and it’s our responsibility to take that same energy home and fight the blockade,” she said.
Author Bio:
This article was produced in partnership by Peoples Dispatch and Globetrotter.
Walter Smolarek is a Philadelphia-based journalist and activist, covering both political developments inside the United States as well as the international activities of U.S. imperialism. Since becoming involved in the movement against the Iraq War as a high school student, he has also participated as an organizer in social movements ranging from Occupy Wall Street in 2011 to the 2014-2015 wave of the Black Lives Matter movement and ongoing mutual aid relief efforts in the face of the coronavirus pandemic. He is a contributor to BreakThrough News, currently serves as the editor of Liberation newspaper, and is the managing editor of LiberationNews.org.
Source: Globetrotter
Why Julian Assange Is At The Vanguard For World Press Freedom
We celebrate World Press Freedom Day in May as a reminder that the role of news organizations is to speak truth to power. Not for manufacturing consent—to use Chomsky’s famous words—for the government and the ruling classes.
It’s an occasion to remember three people who exemplify the need to speak the truth: Daniel Ellsberg of Pentagon Papers fame and Julian Assange of WikiLeaks; and also of Chelsea Manning, without whom we would not have the proof of what the United States was doing, not only in Iraq and Afghanistan but all across the globe. In doing so, I will also deal with the changing nature of government “secrets”, what outing them means then and now.
In today’s day and world, just as the scale of the government’s powers to pry into our lives and activities has increased exponentially—for example, NSA’s Prism and NSO’s Pegasus—so has the scale of the leaks. Ellsberg’s Pentagon Papers were a mere 7,000 pages, and he photocopied them by hand (Daniel Ellsberg, The Doomsday Machine: Confessions of a Nuclear War Planner). Chelsea Manning’s “papers”, which Assange outed, earning the U.S. government’s enmity, consisted of about 750,000 documents (Iraq War logs, Afghanistan War logs and U.S. diplomatic cables). Manning used her computer to copy this enormous cache of data. Ellsberg had one of the highest security clearances in the U.S. government. Snowden, a system administrator, is assumed to have “exfiltrated” more than a million NSA documents.
Manning was low down in the military ranks and a mere corporal. Assange had identified one key characteristic of our epoch: the digital revolution means the enormous centralization of information and also the ease with which it can release. In a conference in 1984, Stewart Brand, an author, in a conversation with Steve Wozniak, the co-founder of Apple, had brought this duality of information in the digital age: the centralization of information as it is so valuable for the rulers. And also the ease of its duplication and therefore liberating it from the rulers. This is why Assange set up WikiLeaks. People, who had access to this valuable information stored in “secure” government vaults, could use WikiLeaks to reach the people. Both use the power of digital technologies and their ability to produce copies but for completely different purposes.
In 1971, a little over 50 years ago that Daniel Ellsberg leaked a study carried out by the U.S. Defense Department—the Pentagon Papers—on the Vietnam War to the New York Times and subsequently to a host of other news organizations. The anti-Vietnam War movement, which had exploded in the United States then, with cascading effects around the world for my generation, had turned Ellsberg into a radical. Just as it did many of us around the world who demonstrated against the United States and its war. The Vietnam War had discredited the U.S. empire and produced a radical generation, of which Daniel Ellsberg was a proud member.
The Pentagon Papers laid out in detail why the Vietnam War was already a lost cause and why Vietnamese people would defeat the neocolonial puppet government of Ngo Dinh Diem backed by the United States in South Vietnam. Though the study was completed in 1968 that the United States could not win, the United States had enlarged the war from a land and air war against the Vietnamese liberation forces in South Vietnam to the aerial bombardment of North Vietnam and Cambodia as well. Ellsberg believed that if the U.S. public learned the truth about the Vietnam War, they would help stop the war. This is why he, and a former colleague Anthony Russo, shared the Pentagon papers with the press. The U.S. people, he believed, had a right to know about the war being waged in their name.
The exposure of Pentagon papers helped the anti-war movement but did not stop the war. It took another four years—April 1975—before Vietnamese freedom fighters liberated Saigon. The pictures of the U.S. forces leaving in ignominy, clinging to helicopters as they lifted off from the roof of the U.S. embassy, are similar to what we saw recently in Kabul.
By the time we reached the Iraq War, the world of information had changed. Information was no longer in paper form. Copies were also not on paper. Digitizing information meant that enormous amounts could be collected, stored and used in real-time for the purpose of war: both its physical-kinetic variety and also the information war. The full power of the United States, its technology might, and its money power could be wielded to build not only the U.S. war machine but also what we now call the surveillance state. Not simply its invasion of every aspect of our lives but also in creating new, invisible hands of the Ministry of Truth. This is an information war of a different kind than in the days of Ellsberg photocopying the Pentagon Papers.
This is the world that Assange saw and understood. If Ellsberg understood the world of power, Assange understood the changing nature of how information is created in vast amounts continuously by the government, stored and transmitted. The very nature of technology that permits this almost costless duplication of information and its flows also makes it vulnerable to being shared and made available to the public. Read more
Noam Chomsky Speaks On What ChatGPT Is Really Good For
The subset of artificial intelligence known as Large Language Models can’t tell us anything about human language learning, but it excels at misleading the uninformed.
Artificial intelligence (AI) is sweeping the world. It is transforming every walk of life and raising in the process major ethical concerns for society and the future of humanity. ChatGPT, which is dominating social media, is an AI-powered chatbot developed by OpenAI. It is a subset of machine learning and relies on what is called Large Language Models that can generate human-like responses. The potential application for such technology is indeed enormous, which is why there are already calls to regulate AI like ChatGPT.
Can AI outsmart humans? Does it pose public threats? Indeed, can AI become an existential threat? The world’s preeminent linguist Noam Chomsky, and one of the most esteemed public intellectuals of all time, whose intellectual stature has been compared to that of Galileo, Newton, and Descartes, tackles these nagging questions in the interview that follows.
C. J. Polychroniou: As a scientific discipline, artificial intelligence (AI) dates back to the 1950s, but over the last couple of decades it has been making inroads into all sort of fields, including banking, insurance, auto manufacturing, music, and defense. In fact, the use of AI techniques has been shown in some instance to surpass human capabilities, such as in a game of chess. Are machines likely to become smarter than humans?
Noam Chomsky: Just to clarify terminology, the term “machine” here means program, basically a theory written in a notation that can be executed by a computer–and an unusual kind of theory in interesting ways that we can put aside here.
We can make a rough distinction between pure engineering and science. There is no sharp boundary, but it’s a useful first approximation. Pure engineering seeks to produce a product that may be of some use. Science seeks understanding. If the topic is human intelligence, or cognitive capacities of other organisms, science seeks understanding of these biological systems.
As I understand them, the founders of AI–Alan Turing, Herbert Simon, Marvin Minsky, and others–regarded it as science, part of the then-emerging cognitive sciences, making use of new technologies and discoveries in the mathematical theory of computation to advance understanding. Over the years those concerns have faded and have largely been displaced by an engineering orientation. The earlier concerns are now commonly dismissed, sometimes condescendingly, as GOFAI–good old-fashioned AI.
Continuing with the question, is it likely that programs will be devised that surpass human capabilities? We have to be careful about the word “capabilities,” for reasons to which I’ll return. But if we take the term to refer to human performance, then the answer is: definitely yes. In fact, they have long existed: the calculator in a laptop, for example. It can far exceed what humans can do, if only because of lack of time and memory. For closed systems like chess, it was well understood in the ‘50s that sooner or later, with the advance of massive computing capacities and a long period of preparation, a program could be devised to defeat a grandmaster who is playing with a bound on memory and time. The achievement years later was pretty much PR for IBM. Many biological organisms surpass human cognitive capacities in much deeper ways. The desert ants in my backyard have minuscule brains, but far exceed human navigational capacities, in principle, not just performance. There is no Great Chain of Being with humans at the top.
The products of AI engineering are being used in many fields, for better or for worse. Even simple and familiar ones can be quite useful: in the language area, programs like autofill, live transcription, google translate, among others. With vastly greater computing power and more sophisticated programming, there should be other useful applications, in the sciences as well. There already have been some: Assisting in the study of protein folding is one recent case where massive and rapid search technology has helped scientists to deal with a critical and recalcitrant problem.
Engineering projects can be useful, or harmful. Both questions arise in the case of engineering AI. Current work with Large Language Models (LLMs), including chatbots, provides tools for disinformation, defamation, and misleading the uninformed. The threats are enhanced when they are combined with artificial images and replication of voice. With different concerns in mind, tens of thousands of AI researchers have recently called for a moratorium on development because of potential dangers they perceive.
As always, possible benefits of technology have to be weighed against potential costs.
Quite different questions arise when we turn to AI and science. Here caution is necessary because of exorbitant and reckless claims, often amplified in the media. To clarify the issues, let’s consider cases, some hypothetical, some real.
I mentioned insect navigation, which is an astonishing achievement. Insect scientists have made much progress in studying how it is achieved, though the neurophysiology, a very difficult matter, remains elusive, along with evolution of the systems. The same is true of the amazing feats of birds and sea turtles that travel thousands of miles and unerringly return to the place of origin.
Suppose Tom Jones, a proponent of engineering AI, comes along and says: “Your work has all been refuted. The problem is solved. Commercial airline pilots achieve the same or even better results all the time.”
If even bothering to respond, we’d laugh.
Understanding The Controversy And Legality Of ‘Overseas Police Stations’

John P. Ruehl
The centers have highlighted China’s growing influence, as well as the increasing legal complexity of managing citizens and dual citizens in Chinese diaspora communities.
The apprehension of two men in New York on April 16, 2023, marked the first known U.S. arrests in connection with Chinese overseas police stations. Both men were working in a building in Manhattan’s Chinatown rented by the America ChangLe Association, a charity that had its tax-exempt status revoked in May 2022. More Chinese police stations are believed to be operating across the U.S.—though, like in other countries, not all their locations are known.
While foreign intelligence agencies conduct extensive espionage operations in other countries, domestic law enforcement agencies are also occasionally active abroad. The FBI trained many Latin American police units throughout the Cold War and has been covertly active in the region for decades. In 2020, Russia also offered to send a police force to Belarus during mass protests against Belarusian President Alexander Lukashenko, who blamed the West for trying to foment a color revolution.
However, the scale of China’s international program and the scope of its responsibilities is notable. Run primarily by ethnic Chinese residents, the main concern of these stations appears to be managing the more than 10.5 million Chinese citizens living overseas, and to a lesser extent the 35 to 60 million people in the Chinese diaspora. The considerable size of Chinese overseas communities has allowed Beijing to field an extensive global presence through these stations.
China’s first known use of these stations occurred in 2004 with the establishment of the Community and Police Cooperation Center in Johannesburg, following several attacks on Chinese citizens and businesses. The center opened with the blessing of the South African government, and more than a dozen have since opened in the country. As in other countries, they help Chinese citizens obtain documents, assist in criminal matters, integrate into the country, as well as offer “security, fire, and ambulance teams.” The Chinese government maintains that they are not police stations but instead function as “service centers.”
Two reports, released in September and December 2022 by the human rights organization Safeguard Defenders, indicated that there are now more than 100 overseas Chinese stations active in more than 50 countries. Managed by China’s Ministry of Public Security, the stations are operated by police agencies from three Chinese provinces (Jiangsu, Zhejiang, and Fujian) and are divided into centers, which are greater in scale, and liaisons, which have a lower profile but are more numerous.
Though the stations had previously drawn little attention, the reports have made Western countries far more wary of them in the context of intensifying geopolitical tensions with China over the last few years. There are also fears that the stations act as part of China’s United Front system to build political, economic, and cultural connections to influence other countries.
The stations have also brought increased Western attention due to their role in convincing Chinese citizens to return to China to face legal charges. Now known as Operation Fox Hunt, Safeguard Defenders estimates that from April 2021 to July 2022, 230,000 Chinese citizens were persuaded or coerced into returning to China, with China’s Ministry of Public Security itself stating that 210,000 citizens returned in 2021. Western officials had already criticized China for abusing Interpol’s Red Notice system to arrest and extradite citizens abroad for political purposes, while Operation Fox Hunt has allowed Chinese officials to bypass Interpol and deal directly with its own citizens. Read more
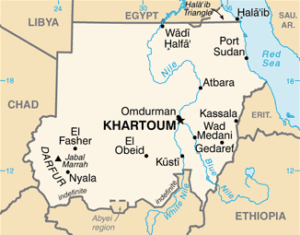
After Years Of Attacking Protesters, Sudan’s Army And Paramilitary RSF Turn On Each Other
More than 500 people have been killed and 4,000 injured since fighting broke out between the Sudanese Armed Forces (SAF) and the paramilitary Rapid Support Forces (RSF) on April 15.
Groups such as the Sudan Doctors Union are worried the fighting could escalate after the evacuation of foreign nationals. Thousands have already fled the country. Over 69 percent of the hospitals in and around the conflict zones are inoperable. There is a severe shortage of medicine, food, water, and electricity.
The fighting is the latest in a series of political convulsions since massive pro-democracy protests overthrew long-time dictator Omar al-Bashir in April 2019. Army chief General Abdel-Fattah Burhan, who is the chair of the ruling military junta, and his deputy and RSF head, General Mohamed Hamdan Dagalo, aka Hemeti, were key members of Bashir’s regime. The RSF was formed out of janjaweed militias who were responsible for mass killings in Darfur during Bashir’s reign.
Burhan and Hemeti took over de facto control after Bashir’s fall and were responsible for the massacre of more than 100 protesters who were demanding civilian rule at a sit-in in Khartoum in June 2019. In its aftermath, they negotiated with right-wing parties in the Forces for Freedom and Change (FFC) coalition and inaugurated a civilian-military transitional government in August.
While this government had a civilian Prime Minister, Abdalla Hamdok, defense, police, and foreign policy were under the control of the army, with Burhan heading a ‘Sovereignty Council.’ The army controls a substantial chunk of the economy while the RSF has gorged on the mineral wealth of Darfur.
The transitional arrangement was supposed to pave the way for civilian rule. Instead, in October 2021, Burhan and Hemeti took complete control in a coup.
Throughout the years since the coup, protesters took to the streets, often in the hundreds of thousands, refusing any compromise with the junta and demanding genuine democracy and civilian control of the military. The protests were spearheaded by the Resistance Committees (RCs), a network of over 5,000 neighborhood organizations. Left forces, including the Sudanese Communist Party, were a key force too. Over 120 people were killed in the attacks on demonstrations in the months following the October 2021 coup.
Disregarding popular sentiment against any negotiations with the junta, the international community—the UN, U.S., UK, European Union, African Union, and the regional Intergovernmental Authority on Development—supported renewed talks between the junta and the FFC.
This negotiation led to the Framework Agreement in December 2022, which was to be concluded with a final political agreement that would have led to the formation of another joint government with civilians on April 11, 2023.
This plan did not materialize as the SAF and RSF turned on each other after disagreeing over the timespan for the integration of the latter into the former.
The Sudanese Communist Party has reiterated its rejection of any compromise with the junta. It maintains that international support for another power-sharing compromise after the October coup served to legitimize the junta, which eventually led to this infighting.
Author Bio:
This article was produced in partnership by Peoples Dispatch and Globetrotter.
Pavan Kulkarni and Prasanth Radhakrishnan are journalists with Peoples Dispatch and Newsclick.
Source: Globetrotter
Gilbert Achcar On The New Cold War
The risk of a new Cold War has greatly increased in recent times, not only because of Russia’s invasion of Ukraine but also because the US has acknowledged China as a superpower rival that needs to be contained. This is the version about current international affairs that one encounters among mainstream analysts. However, Lebanese socialist scholar Gilbert Achcar claims that this interpretation of interstate relations in today’s world is a misrepresentation of the evolution of global politics since the official end of the period known as the Cold War, which lasted from 1947-1991, and rests on a confusing notion around the issue of a “new Cold War.” Indeed, in the interview that follows, Achcar argues that a New Cold War has been underway since the late 1990s and we are now at a stage where it could get hot.
Gilbert Achcar is professor of development studies and international relations at the School of Oriental and African Studies, University of London. He is the author of many books, including The People Want: A Radical Exploration of the Arab Uprising; The Clash of Barbarisms: The Making of the New World Disorder; Perilous Power: The Middle East and U.S. Foreign Policy (co-authored with Noam Chomsky), and Marxism, Orientalism, Cosmopolitanism. His latest book, which was just released, is The New Cold War: The United States, Russia and China from Kosovo to Ukraine (Haymarket Books 2023).
C. J. Polychroniou: Russia’s invasion of Ukraine and its partnership with China have led many commentators to speak of the beginning of a New Cold War. However, in your newly released book The New Cold War: The United States, Russia, and China from Kosovo to Ukraine, you argue that a new geopolitical East-West divide, and thus the emergence of a New Cold War, can be traced back to the late 1990s, and specifically to the Kosovo war. Let’s start with your understanding of the term “cold war” because I can see many objecting to your interpretation of the interaction of states in the global interstate system prior to Russia’s invasion of Ukraine.
Gilbert Achcar: There is a lot of confusion indeed around the issue of a new cold war. The uses of the expression did not start proliferating now, but since 2014 regarding US relations with Russia and since Trump for those with China. The range of opinions remained the same though, between those who believe that we’re in the thick of it, those who believe that it has only started now with the invasion of Ukraine, and those who are still warning of it as a potential outcome! What is right in all this, however, is that the notion of “cold war” is not conflated with the ideological and systemic opposition that existed between the Soviet-led and the US-led blocs. The origins of the expression “cold war” and of the notion of a New Cold War are both discussed in detail in my book.
Basically, a “cold war” is a situation in which a country maintains a state of preparation for war without being (yet) engaged in a “hot war.” In other words, the arms race is what made the Cold War be called as such, and I have explained since the late 1990s how the United States had decided to maintain a level of military expenditure based on the scenario of a war simultaneously waged against Russia and China. This decision was related to other provocative stances by Washington, which led me to identify the beginning of what I called the New Cold War in 1999. What happened since could only confirm this diagnosis, and it is rather amusing that today, when the world is as close to a very hot world war as it has ever been since 1945, some are still reluctant to call a spade a spade!
CJP: Who is the real enemy for Washington at the time you situate the genesis of the New Cold War, and why is the war in Kosovo such a dramatic turning point in the post-Cold War world?
GA: There were a lot of comments after the demise of the USSR about Washington’s need to invent a new global enemy. Some believed that “terrorism” had solved the problem, but “terrorism” is in no way the kind of “peer competitor” that Washington needs to secure the allegiance of its Cold War allies, which Zbigniew Brzezinski famously called its “vassals.” By basing its actual behavior on the assumption that both Russia and China were potential enemies, the United States has recreated tensions with Russia—and created new ones with China, after cooperating with it against the USSR during the last 15 years of the Cold War.
The Kosovo war was decisive because it shattered any illusions Moscow and Beijing might have had about the “new world order” promised by George Bush Sr. in 1990, when he was preparing for the first US-led war on Iraq conducted in the name of international law and sanctioned by a UN Security Council resolution that Moscow approved and on which Beijing abstained. Bush Sr.—in a famous speech delivered, by an irony of history, on September 11, 1990—had promised that, from then on, the world would be “quite different from the one we’ve known: a world where the rule of law supplants the rule of the jungle.” Moscow and Beijing hoped that the UN would henceforth play the role for which it had been initially designed, thus giving them a veto right about the use of force in international relations. Likewise, Bill Clinton’s administration had assured Moscow that NATO’s enlargement to Poland, Hungary and the Czech Republic was not intended against Russia. And yet, the same year 1999 when that enlargement was sealed is the year when NATO launched its first war ever, the Kosovo war, circumventing the UNSC and thus violating international law. Read more
- Page 2 of 2
- previous page
- 1
- 2